Page 347 - ANUAL REPORT MOH 2017
P. 347
• GAP EQUIPMENT SUPPLY STATUS
Under the agreement, QMS is also responsible to supply, deliver, install, testing and commissioning of
GAP equipment. The procurement of the GAP equipment is divided into two (2) types, which are New
Biomedical Equipment (NBE) and Purchased Biomedical Equipment (PBE). For NBE, the equipment
will be leased out to the Government for a period of 8 years after which the equipment ownership is
belonging to the Government. For PBE, the Government will own the equipment after it has been
supplied. All of the equipment will be supplied in 12 batches within a 3 years period.
The supply of GAP equipment has been started on September to November 2016 for batch 1, December
2016 to February 2017 for batch 2, March to May 2017 for batch 3, June to August 2017 for batch 4
and September to November 2017 for batch 5. Table 14 shows the total number of equipment being
supplied to Government clinics in Batch 1 to 5 by state.
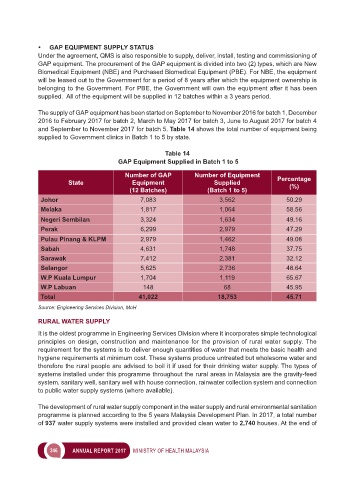
Table 14
GAP Equipment Supplied in Batch 1 to 5
Number of GAP Number of Equipment
State Equipment Supplied Percentage
(%)
(12 Batches) (Batch 1 to 5)
Johor 7,083 3,562 50.29
Melaka 1,817 1,064 58.56
Negeri Sembilan 3,324 1,634 49.16
Perak 6,299 2,979 47.29
Pulau Pinang & KLPM 2,979 1,462 49.08
Sabah 4,631 1,748 37.75
Sarawak 7,412 2,381 32.12
Selangor 5,625 2,736 48.64
W.P Kuala Lumpur 1,704 1,119 65.67
W.P Labuan 148 68 45.95
Total 41,022 18,753 45.71
Source: Engineering Services Division, MoH
RURAL WATER SUPPLY
It is the oldest programme in Engineering Services Division where it incorporates simple technological
principles on design, construction and maintenance for the provision of rural water supply. The
requirement for the systems is to deliver enough quantities of water that meets the basic health and
hygiene requirements at minimum cost. These systems produce untreated but wholesome water and
therefore the rural people are advised to boil it if used for their drinking water supply. The types of
systems installed under this programme throughout the rural areas in Malaysia are the gravity-feed
system, sanitary well, sanitary well with house connection, rainwater collection system and connection
to public water supply systems (where available).
The development of rural water supply component in the water supply and rural environmental sanitation
programme is planned according to the 5 years Malaysia Development Plan. In 2017, a total number
of 937 water supply systems were installed and provided clean water to 2,740 houses. At the end of
346 ANNUAL REPORT 2017 MINISTRY OF HEALTH MALAYSIA