Page 159 - Engineering Mathematics Workbook_Final
P. 159
Complex Variables
1 − 1 px
(
2
f ( ) z = log x + y 2 ) + i tan
2 y
is analytic is ______. [JNU]
(c)
159. If ( ) ( x + ay 2 ) + ibxy is
f z =
2
complex analytic function of
z = x iy , where i = − 1, then
+
(a) a = − 1, b = − 1
(b) a = − 1, b =
2
(d)
(c) a = 1, b = 2
(d) a = 2, b = 2 [GATE 2017]
)
)
160. If ( , x y and ( , x y are functions
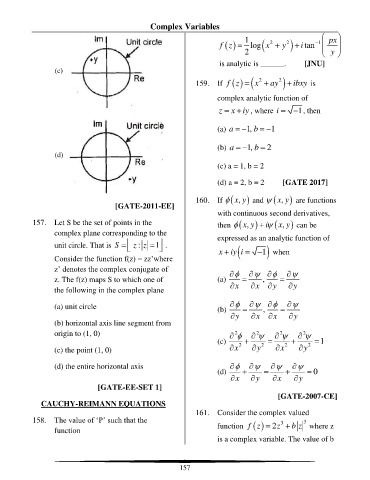
[GATE-2011-EE]
with continuous second derivatives,
)
157. Let S be the set of points in the then ( ,x y ) i + ( ,x y can be
complex plane corresponding to the expressed as an analytic function of
unit circle. That is S = : z z = 1 . x iy i = − 1 when
(
)
+
Consider the function f(z) = zz’where
z’ denotes the complex conjugate of
z. The f(z) maps S to which one of (a) = , =
the following in the complex plane x x y y
(a) unit circle (b) = =
,
y x x y
(b) horizontal axis line segment from
origin to (1, 0) 2 2 2 2
(c) 2 + 2 = 2 + 2 = 1
(c) the point (1, 0) x y x y
(d) the entire horizontal axis + = + =
(d) x y x y 0
[GATE-EE-SET 1]
[GATE-2007-CE]
CAUCHY-REIMANN EQUATIONS
161. Consider the complex valued
158. The value of ‘P’ such that the function ( ) 2f z = z + 3 3
function b z where z
is a complex variable. The value of b
157