Page 84 - DK Children's Encyclopedia
P. 84
Early humans SEE ALSO
▸ ▸ Africa p.12
▸ ▸ Evolution p.95
The first humans were similar to apes, such as gorillas and ▸ ▸ Fossils p.111
chimpanzees. Over millions of years, they learned to walk ▸ ▸ Monkeys
on two legs and got smarter as their brains grew larger. and apes p.170
They also lost most of their body hair, slowly becoming ▸ ▸ Exploration
more like the humans we are today. pp.180–181
▸ ▸ Stone Age p.243
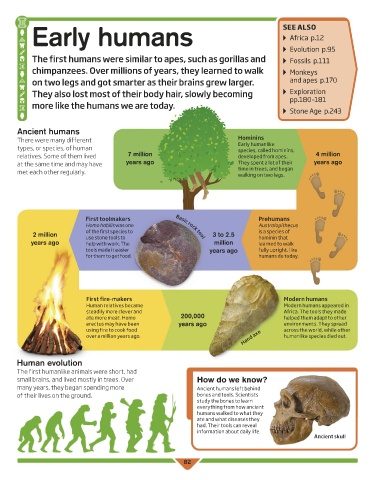
Ancient humans
There were many different Hominins
types, or species, of human Early humanlike
species, called hominins,
relatives. Some of them lived 7 million developed from apes. 4 million
at the same time and may have years ago They spent a lot of their years ago
met each other regularly. time in trees, and began
walking on two legs.
First toolmakers Prehumans
Homo habilis was one Basic rock tool Australopithecus
of the first species to is a species of
2 million use stone tools to 3 to 2.5 hominin that
years ago help with work. The million learned to walk
tools made it easier years ago fully upright, like
for them to get food. humans do today.
First fire-makers Modern humans
Human relatives became Modern humans appeared in
steadily more clever and Africa. The tools they made
ate more meat. Homo 200,000 helped them adapt to other
erectus may have been years ago environments. They spread
using fire to cook food across the world, while other
over a million years ago. Hand axe humanlike species died out.
Human evolution
The first humanlike animals were short, had
small brains, and lived mostly in trees. Over How do we know?
many years, they began spending more Ancient humans left behind
of their lives on the ground. bones and tools. Scientists
study the bones to learn
everything from how ancient
humans walked to what they
ate and what diseases they
had. Their tools can reveal
information about daily life.
Ancient skull
82
US_082_Early_Humans.indd 82 16/05/2017 09:47