Page 70 - Advanced Course
P. 70
KNX ADVANCED COURSE
4 Integrating air conditioning systems
4.1 Introduction
Because of the use of KNX across different applications and its high level of integration,
one needs to certainly also familiarize oneself with the connection of air conditioners to
KNX systems. This is especially relevant in climate zones where temperatures are higher
and heating is less of an issue. However, the need for air conditioning may also arise in
glass buildings, where room temperatures can increase significantly during the summer.
In buildings that house both heating and air conditioning systems, you often find that these
systems are managed separately, sometimes even by different people. In order to avoid
conflicting approaches in such a situation, it is highly useful to integrate all components
into a KNX system. By doing so, you can avoid that the air conditioning system cools
while the heating at the same time tries to keep the temperature level constant by
simultaneously heating the room.
4.2 Technical Design
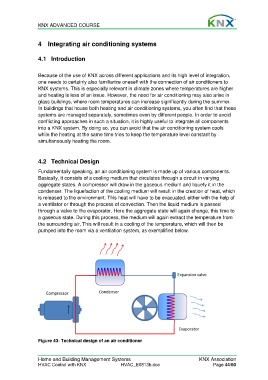
Fundamentally speaking, an air conditioning system is made up of various components.
Basically, it consists of a cooling medium that circulates through a circuit in varying
aggregate states. A compressor will draw in the gaseous medium and liquefy it in the
condenser. The liquefaction of the cooling medium will result in the creation of heat, which
is released to the environment. This heat will have to be evacuated, either with the help of
a ventilator or through the process of convection. Then the liquid medium is passed
through a valve to the evaporator. Here the aggregate state will again change, this time to
a gaseous state. During this process, the medium will again extract the temperature from
the surrounding air. This will result in a cooling of the temperature, which will then be
pumped into the room via a ventilation system, as exemplified below.
Figure 43: Technical design of an air conditioner
Home and Building Management Systems KNX Association
HVAC Control with KNX HVAC_E0813b.doc Page 44/60