Page 33 - Digital Electronics by harish
P. 33
Case 1 : A = 0 and B = 0
In this case, the output ( . B + A .) = (1 . 0 + 0 . 1) = (0 + 0) = 0
Case 2 : A = 0 and B = 1
In this case, the output ( . B + A .) = (1 . 1) + 0 . 0) = (1 + 0) = 1
Case 3 : A = 1 and B = 0
In this case, the output ( . B + A .) = (0 . 0 + 1 . 1) = (0 + 1) = 1
Case 4 : A = 1 and B = 1
In this case, the output ( . B + A .) = (0 .1 + 1 . 0) = (0 + 0) = 0
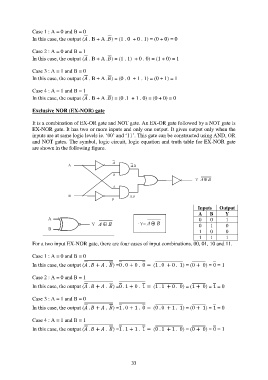
Exclusive NOR (EX-NOR) gate
It is a combination of EX-OR gate and NOT gate. An EX-OR gate followed by a NOT gate is
EX-NOR gate. It has two or more inputs and only one output. It gives output only when the
inputs are at same logic levels ie. „00‟ and „11‟. This gate can be constructed using AND, OR
and NOT gates. The symbol, logic circuit, logic equation and truth table for EX-NOR gate
are shown in the following figure.
Inputs Output
A B Y
0 0 1
0 1 0
1 0 0
1 1 1
For a two input EX-NOR gate, there are four cases of input combinations, 00, 01, 10 and 11.
Case 1 : A = 0 and B = 0
In this case, the output ( . + . ) =0 . 0 + 0 . 0 = (1 . 0 + 0 . 1) = (0 + 0) = 0 = 1
Case 2 : A = 0 and B = 1
In this case, the output ( . + . ) =0 . 1 + 0 . 1 = (1 . 1 + 0 . 0) = (1 + 0) = 1 = 0
Case 3 : A = 1 and B = 0
In this case, the output ( . + . ) =1 . 0 + 1 . 0 = (0 . 0 + 1 . 1) = (0 + 1) = 1 = 0
Case 4 : A = 1 and B = 1
In this case, the output ( . + . ) =1 . 1 + 1 . 1 = (0 . 1 + 1 . 0) = (0 + 0) = 0 = 1
33