Page 34 - Drug Discovery and Development: Prospects and Challenges
P. 34
Biopharmaceutical Classification System (BCS) is an experimental technique to determine the
permeability and solubility of a particular product under controlled settings. Based on their aqueous
solubility and intestinal permeability, the drugs are classified into four classes. In addition to the BCS
classification, the input from pre-formulation studies would benefit the formulation by providing a
detailed solubility profile, polymorph status, intended dosage form, target dose, dosing schedule, drug
stability, excipient compatibility, and understanding of the transporter and metabolic pathways.
Drugs in BCS are classified as high permeability but low solubility. In order to improve the
performance of these drugs, a special technique is required to increase the surface area, such as particle
size reduction, using a solid solution, or solid dispersion. Nowadays, new technologies are available
to modify the formulation using solvents and/or surfactants. One of the strategies is to encapsulate the
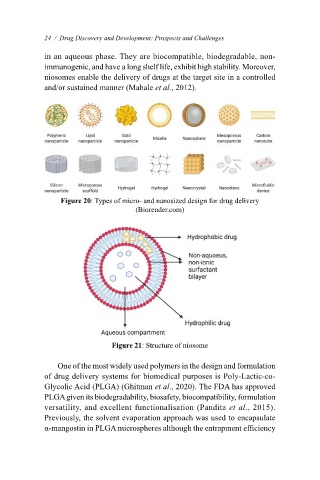
drugs with Nanotechnology Drug Delivery System (NDDS) (Figure 20). NDDS refers to a material
that has at least one dimension that falls under the nanometer scale (1–100 nm) or is made with basic
units in three-dimensional space (Deng, 2020).
Nanotechnology has become a useful tool to regulate the delivery rate and target the drug
delivery to a specific location, such as using vesicle nanocarrier, for instance, liposomes and niosomes.
Liposome comprises cholesterol and phospholipid, while niosome uses cholesterol and non-ionic
surfactant. The active principle in liposomes and niosome involves the encapsulation of the drug in
vesicle components of hydrophilic and hydrophobic areas. Niosome (Figure 21) is made up of bilayer
24 / Drug Discovery and Development: Prospects and Challenges
structures and formed by self-association of non-ionic surfactant and cholesterol in an aqueous phase.
They are biocompatible, biodegradable, non-immunogenic, and have a long shelf life, exhibit high
in an aqueous phase. They are biocompatible, biodegradable, non-
stability. Moreover, niosomes enable the delivery of drugs at the target site in a controlled and/or
immunogenic, and have a long shelf life, exhibit high stability. Moreover,
sustained manner (Mahale et al., 2012).
niosomes enable the delivery of drugs at the target site in a controlled
and/or sustained manner (Mahale et al., 2012).
Figure 20: Types of micro- and nanosized design for drug delivery (Biorender.com)
Figure 20: Types of micro- and nanosized design for drug delivery
(Biorender.com)
29
Figure 21: Structure of niosome
Figure 21: Structure of niosome
One of the most widely used polymers in the design and formulation
One of the most widely used polymers in the design and formulation of drug delivery systems
of drug delivery systems for biomedical purposes is Poly-Lactic-co-
for biomedical purposes is Poly-Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid (PLGA) (Ghitman et al., 2020). The FDA
Glycolic Acid (PLGA) (Ghitman et al., 2020). The FDA has approved
PLGA given its biodegradability, biosafety, biocompatibility, formulation
has approved PLGA given its biodegradability, biosafety, biocompatibility, formulation versatility,
versatility, and excellent functionalisation (Pandita et al., 2015).
and excellent functionalisation (Pandita et al., 2015). Previously, the solvent evaporation approach
Previously, the solvent evaporation approach was used to encapsulate
was used to encapsulate α-mangostin in PLGA microspheres although the entrapment efficiency was
α-mangostin in PLGA microspheres although the entrapment efficiency
low. Considering that α-mangostin is soluble in organic solvent due to its hydrophobic nature, the
microsphere formulation could be a potential α-mangostin micro-carrier delivery system to treat lung
tissue cancer (Ali et al., 2013).
Although oral intake is the most preferable route of drug delivery, more than 70% of the active
pharmaceutical ingredients are poorly water-soluble or lipophilic compounds, which prevent them
from reaching the desired efficacy. As a result, the bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs is
significantly affected. These compounds are typically grouped as BCS class II or class IV compounds
(Anwer et al., 2021). To improve the rate of absorption and solubility, the Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug
Delivery System (SNEDDS) was developed as an alternative formulation method. SNEDDS is a
relatively new emulsion technology with the purpose to improve the rate and extent of absorption of
poorly water-soluble drugs. SNEDDS are anhydrous homogeneous liquid mixtures composed of
30