Page 93 - spectroscopic-atlas-5_0-english_Neat
P. 93
Spectroscopic Atlas for Amateur Astronomers 93
20 Spectral Sequence on the AGB
20.1 Evolution of the Stars on the Asymptotic Giant Branch (AGB)
The following simplified presented sequence is applicable for stars with 1 to 8, depending
on the source, even up to about 10 solar masses.
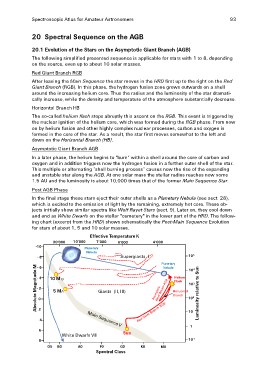
Red Giant Branch RGB
After leaving the Main Sequence the star moves in the HRD first up to the right on the Red
Giant Branch (RGB). In this phase, the hydrogen fusion zone grows outwards on a shell
around the increasing helium core. Thus the radius and the luminosity of the star dramati-
cally increase, while the density and temperature of the atmosphere substantially decrease.
Horizontal Branch HB
The so-called helium flash stops abruptly this ascent on the RGB. This event is triggered by
the nuclear ignition of the helium core, which was formed during the RGB phase. From now
on by helium fusion and other highly complex nuclear processes, carbon and oxygen is
formed in the core of the star. As a result, the star first moves somewhat to the left and
down on the Horizontal Branch (HB).
Asymptotic Giant Branch AGB
In a later phase, the helium begins to "burn" within a shell around the core of carbon and
oxygen and in addition triggers now the hydrogen fusion in a further outer shell of the star.
This multiple or alternating “shell burning process” causes now the rise of the expanding
and unstable star along the AGB. At one solar mass the stellar radius reaches now some
1.5 AU and the luminosity is about 10,000 times that of the former Main Sequence Star.
Post AGB Phase
In the final stage these stars eject their outer shells as a Planetary Nebula (see sect. 28),
which is excited to the emission of light by the remaining, extremely hot core. These ob-
jects initially show similar spectra like Wolf Rayet Stars (sect. 9). Later on, they cool down
and end as White Dwarfs on the stellar "cemetery" in the lower part of the HRD. The follow-
ing chart (excerpt from the HRD) shows schematically the Post-Main Sequence Evolution
for stars of about 1, 5 and 10 solar masses.
Effective Temperature K
30‘000 10‘000 7‘000 6‘000 4‘000
-10 Planetary
Nebula
- 8 Supergiants I 105
104
Planetary
- 6 Nebula
Absolute Magnitude M
- 4 10 M Luminosity relative to SunGiants (II, III)Helium
-2 5M Flash
0 103
Horizontal
Branch
102
2 10
1
4 10-1
6 Sun
White Dwarfs VII
8
O5 B0 A0 F0 G0 K0 M0
Spectral Class