Page 101 - text book form physics kssm 2020
P. 101
Chapter 3
Gravitation
2 3
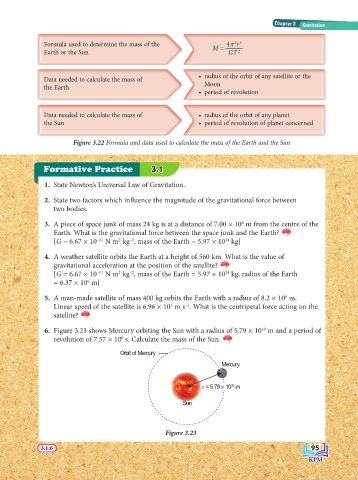
Formula used to determine the mass of the M = 4π r
Earth or the Sun GT 2
• radius of the orbit of any satellite or the
Data needed to calculate the mass of
Moon
the Earth
• period of revolution
Data needed to calculate the mass of • radius of the orbit of any planet
the Sun • period of revolution of planet concerned
Figure 3.22 Formula and data used to calculate the mass of the Earth and the Sun
3.1
Formative Practice 3.1
1. State Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation.
2. State two factors which infl uence the magnitude of the gravitational force between
two bodies.
6
3. A piece of space junk of mass 24 kg is at a distance of 7.00 × 10 m from the centre of the
Earth. What is the gravitational force between the space junk and the Earth?
–11
2
[G = 6.67 × 10 N m kg , mass of the Earth = 5.97 × 10 kg]
–2
24
4. A weather satellite orbits the Earth at a height of 560 km. What is the value of
gravitational acceleration at the position of the satellite?
–2
24
–11
[G = 6.67 × 10 N m kg , mass of the Earth = 5.97 × 10 kg, radius of the Earth
2
6
= 6.37 × 10 m]
5. A man-made satellite of mass 400 kg orbits the Earth with a radius of 8.2 × 10 m.
6
Linear speed of the satellite is 6.96 × 10 m s . What is the centripetal force acting on the p 3 –1
satellite?
10
6. Figure 3.23 shows Mercury orbiting the Sun with a radius of 5.79 × 10 m and a period of
6
revolution of 7.57 × 10 s. Calculate the mass of the Sun.
Orbit of Mercury
Mercury
r = 5.79 × 10 m
10
Sun
Figure 3.23
95
3.1.6
3.1.6 95