Page 106 - text book form physics kssm 2020
P. 106
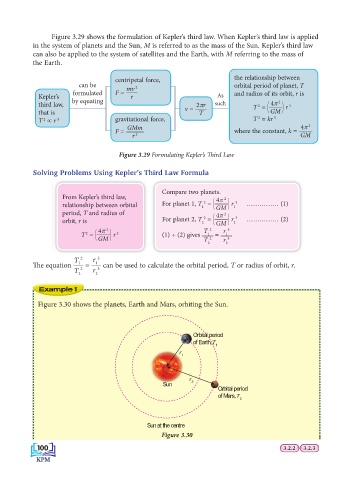
Figure 3.29 shows the formulation of Kepler’s third law. When Kepler’s third law is applied
in the system of planets and the Sun, M is referred to as the mass of the Sun. Kepler’s third law
can also be applied to the system of satellites and the Earth, with M referring to the mass of
the Earth.
centripetal force, the relationship between
can be mv 2 orbital period of planet, T
formulated F = and radius of its orbit, r is
Kepler’s r As
by equating 4π 2
third law, 2πr such 2 3
v = T = r
that is T GM
2
3
2
T ∝ r gravitational force, T = kr 3
GMm 4π 2
F = where the constant, k =
r 2 GM
Figure 3.29 Formulating Kepler’s Th ird Law
Solving Problems Using Kepler’s Third Law Formula
Compare two planets.
From Kepler’s third law, 4π 2
1
r
2
relationship between orbital For planet 1, T = GM 1 3 …………… (1)
period, T and radius of 4π 2
2
2
r
orbit, r is For planet 2, T = GM 2 3 …………… (2)
2
T = 4π 2 r 3 (1) ÷ (2) gives T 1 2 = r 1 3
GM T 2 r 3
2 2
T 2 r 3
Th e equation 1 = 1 can be used to calculate the orbital period, T or radius of orbit, r.
T 2 r 3
2 2
Example 1
Figure 3.30 shows the planets, Earth and Mars, orbiting the Sun.
Orbital period
of Earth,T
1
r
1
r
Sun 2
Orbital period
of Mars,T
2
Sun at the centre
Figure 3.30
100 3.2.2 3.2.3
100
3.2.3
3.2.2