Page 134 - text book form physics kssm 2020
P. 134
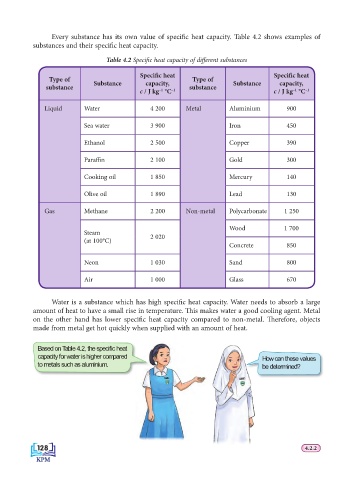
Every substance has its own value of specifi c heat capacity. Table 4.2 shows examples of
substances and their specifi c heat capacity.
Table 4.2 Specifi c heat capacity of diff erent substances
Specifi c heat Specifi c heat
Type of Type of
Substance capacity, Substance capacity,
substance substance
–1
–1
c / J kg °C –1 c / J kg °C –1
Liquid Water 4 200 Metal Aluminium 900
Sea water 3 900 Iron 450
Ethanol 2 500 Copper 390
Paraffi n 2 100 Gold 300
Cooking oil 1 850 Mercury 140
Olive oil 1 890 Lead 130
Gas Methane 2 200 Non-metal Polycarbonate 1 250
Wood 1 700
Steam
2 020
(at 100°C)
Concrete 850
Neon 1 030 Sand 800
Air 1 000 Glass 670
Water is a substance which has high specifi c heat capacity. Water needs to absorb a large
amount of heat to have a small rise in temperature. Th is makes water a good cooling agent. Metal
on the other hand has lower specifi c heat capacity compared to non-metal. Th erefore, objects
made from metal get hot quickly when supplied with an amount of heat.
Based on Table 4.2, the specifi c heat
capacity for water is higher compared How can these values
to metals such as aluminium. be determined?
128
128 4.2.2
4.2.2