Page 191 - text book form physics kssm 2020
P. 191
Chapter 5
Waves
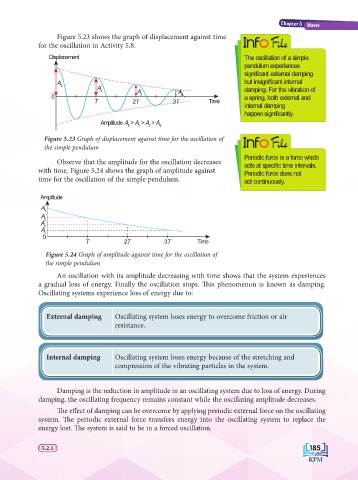
Figure 5.23 shows the graph of displacement against time File
for the oscillation in Activity 5.8.
Displacement The oscillation of a simple
pendulum experiences
signifi cant external damping
A but insignifi cant internal
1 A
2 A A damping. For the vibration of
0 3 4 a spring, both external and
T 2T 3T Time
internal damping
happen signifi cantly.
Amplitude A > A > A > A
1 2 3 4
Figure 5.23 Graph of displacement against time for the oscillation of File
the simple pendulum
Periodic force is a force which
Observe that the amplitude for the oscillation decreases acts at specifi c time intervals.
with time. Figure 5.24 shows the graph of amplitude against Periodic force does not
time for the oscillation of the simple pendulum. act continuously.
Amplitude
A
1
A 2
A 3
A 4
0
T 2T 3T Time
Figure 5.24 Graph of amplitude against time for the oscillation of
the simple pendulum
An oscillation with its amplitude decreasing with time shows that the system experiences
a gradual loss of energy. Finally the oscillation stops. Th is phenomenon is known as damping.
Oscillating systems experience loss of energy due to:
External damping Oscillating system loses energy to overcome friction or air
resistance.
Internal damping Oscillating system loses energy because of the stretching and
compression of the vibrating particles in the system.
Damping is the reduction in amplitude in an oscillating system due to loss of energy. During
damping, the oscillating frequency remains constant while the oscillating amplitude decreases.
Th e eff ect of damping can be overcome by applying periodic external force on the oscillating
system. Th e periodic external force transfers energy into the oscillating system to replace the
energy lost. Th e system is said to be in a forced oscillation.
185
185
185
5.2.1 185
5.2.1