Page 47 - text book form physics kssm 2020
P. 47
Chapter 2 Force and Motion I
Interpreting and Sketching Graphs
Interpreting displacement-time graphs can help to sketch velocity-time graphs and vice versa.
Velocity-time graphs can also be interpreted into acceleration-time graphs and vice versa.
The skill in interpreting and sketching graphs is important to solve linear motion problems.
Study the examples given.
Example 1
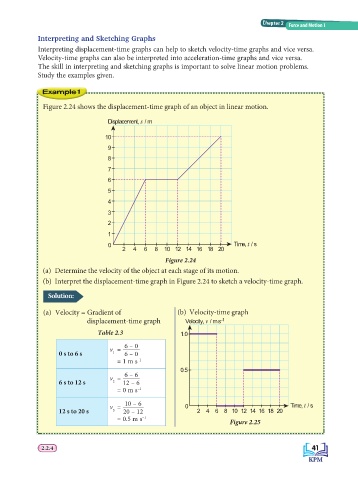
Figure 2.24 shows the displacement-time graph of an object in linear motion.
Displacement, s / m
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0 Time, t / s
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
Figure 2.24
(a) Determine the velocity of the object at each stage of its motion.
(b) Interpret the displacement-time graph in Figure 2.24 to sketch a velocity-time graph.
Solution:
Solution:
(a) Velocity = Gradient of (b) Velocity-time graph
displacement-time graph Velocity, v / m s –1
1.0
Table 2.3
6 – 0
v =
0 s to 6 s 1 6 – 0
= 1 m s –1
0.5
6 – 6
v =
6 s to 12 s 2 12 – 6
= 0 m s –1
10 – 6 Time, t / s
v = 0
12 s to 20 s 3 20 – 12 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
= 0.5 m s –1
Figure 2.25
2.2.4 41 41
2.2.4