Page 44 - text book form physics kssm 2020
P. 44
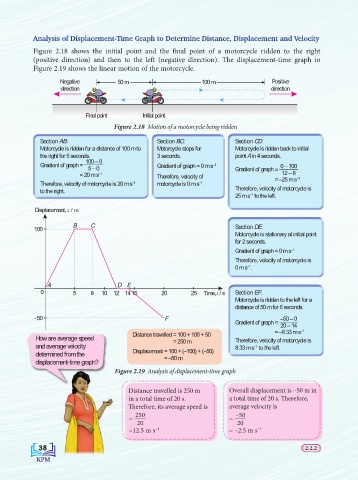
Analysis of Displacement-Time Graph to Determine Distance, Displacement and Velocity
Figure 2.18 shows the initial point and the final point of a motorcycle ridden to the right
(positive direction) and then to the left (negative direction). The displacement-time graph in
Figure 2.19 shows the linear motion of the motorcycle.
Negative 50 m 100 m Positive
direction direction
Final point Initial point
Figure 2.18 Motion of a motorcycle being ridden
Section AB: Section BC: Section CD:
Motorcycle is ridden for a distance of 100 m to Motorcycle stops for Motorcycle is ridden back to initial
the right for 5 seconds. 3 seconds. point A in 4 seconds.
100 – 0
Gradient of graph = Gradient of graph = 0 m s –1 0 – 100
5 – 0 Gradient of graph =
= 20 m s –1 12 – 8
Therefore, velocity of = –25 m s –1
Therefore, velocity of motorcycle is 20 m s –1 motorcycle is 0 m s .
–1
to the right. Therefore, velocity of motorcycle is
–1
25 m s to the left.
Displacement, s / m
B C Section DE:
100
Motorcycle is stationary at initial point
for 2 seconds.
Gradient of graph = 0 m s –1
Therefore, velocity of motorcycle is
0 m s .
–1
A D E
0 5 8 10 12 14 15 20 25 Time, t / s Section EF:
Motorcycle is ridden to the left for a
distance of 50 m for 6 seconds.
–50 F –50 – 0
Gradient of graph = 20 – 14
–1
Distance travelled = 100 + 100 + 50 = –8.33 m s
How are average speed = 250 m Therefore, velocity of motorcycle is
and average velocity 8.33 m s to the left.
–1
determined from the Displacement = 100 + (–100) + (–50)
= –50 m
displacement-time graph?ment-time graph?
Figure 2.19 Analysis of displacement-time graph
F F
Distance travelled is 250 m Overall displacement is –50 m in
in a total time of 20 s. a total time of 20 s. Therefore,
Therefore, its average speed is average velocity is
250 –50
= =
20 20
=12.5 m s –1 = –2.5 m s –1
38
38 2.2.2
2.2.2