Page 48 - text book form physics kssm 2020
P. 48
Example 2
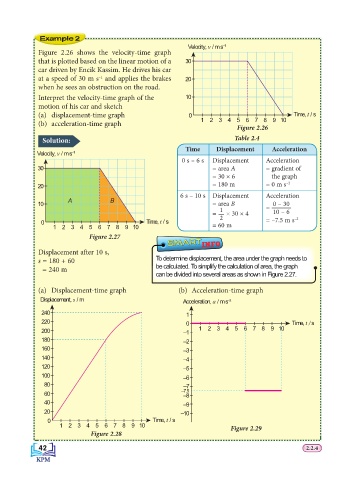
Velocity, v / m s –1
Figure 2.26 shows the velocity-time graph
that is plotted based on the linear motion of a 30
car driven by Encik Kassim. He drives his car
at a speed of 30 m s and applies the brakes 20
–1
when he sees an obstruction on the road.
Interpret the velocity-time graph of the 10
motion of his car and sketch
(a) displacement-time graph 0 Time, t / s
(b) acceleration-time graph 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Figure 2.26
Solution: Table 2.4
Time Displacement Acceleration
Velocity, v / m s –1
0 s – 6 s Displacement Acceleration
30 = area A = gradient of
= 30 × 6 the graph
20 = 180 m = 0 m s –2
6 s – 10 s Displacement Acceleration
A B
10 = area B 0 – 30
1 =
= — × 30 × 4 10 – 6
0 Time, t / s 2 = –7.5 m s –2
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 = 60 m
SMART
SMART
Figure 2.27
INFO
Displacement after 10 s,
s = 180 + 60 To determine displacement, the area under the graph needs to
= 240 m be calculated. To simplify the calculation of area, the graph
can be divided into several areas as shown in Figure 2.27.
(a) Displacement-time graph (b) Acceleration-time graph
Displacement, s / m Acceleration, a / m s –2
240 1
220 0 Time, t / s
200 –1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
180 –2
160 –3
140 –4
120 –5
100 –6
80 –7
60 –7.5
–8
40 –9
20 –10
0 Time, t / s
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Figure 2.29
Figure 2.28
42 2.2.4
42
2.2.4