Page 45 - text book form physics kssm 2020
P. 45
Chapter 2 Force and Motion I
Analysis of Velocity-Time Graph to Determine Distance, Displacement, Velocity
and Acceleration
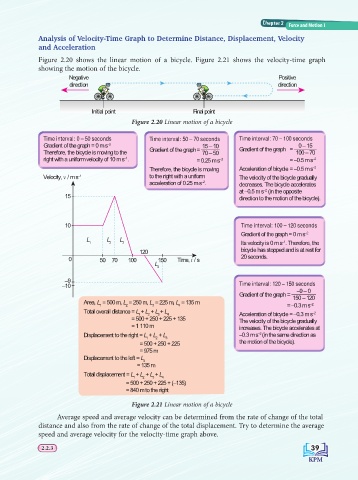
Figure 2.20 shows the linear motion of a bicycle. Figure 2.21 shows the velocity-time graph
showing the motion of the bicycle.
Negative Positive
direction direction
Initial point Final point
Figure 2.20 Linear motion of a bicycle
Time interval: 0 – 50 seconds Time interval: 50 – 70 seconds Time interval: 70 – 100 seconds
Gradient of the graph = 0 m s –2 15 – 10 0 – 15
Therefore, the bicycle is moving to the Gradient of the graph = 70 – 50 Gradient of the graph = 100 – 70
right with a uniform velocity of 10 m s . = 0.25 m s –2 = –0.5 m s
–1
–2
Therefore, the bicycle is moving Acceleration of bicycle = –0.5 m s –2
–1
Velocity, v / m s to the right with a uniform The velocity of the bicycle gradually
acceleration of 0.25 m s . decreases. The bicycle accelerates
–2
at –0.5 m s (in the opposite
–2
15 direction to the motion of the bicycle).
10 Time interval: 100 – 120 seconds
Gradient of the graph = 0 m s –2
L L L
–1
1 2 3 Its velocity is 0 m s . Therefore, the
120 bicycle has stopped and is at rest for
0 50 70 100 150 Time, t / s 20 seconds.
L
4
–9
–10 Time interval: 120 – 150 seconds
–9 – 0
Gradient of the graph = 150 – 120
Area, L = 500 m, L = 250 m, L = 225 m, L = 135 m
–2
1 2 3 4 = –0.3 m s
Total overall distance = L + L + L + L 4 Acceleration of bicycle = –0.3 m s –2
3
2
1
= 500 + 250 + 225 + 135 The velocity of the bicycle gradually
= 1 110 m increases. The bicycle accelerates at
–2
Displacement to the right = L + L + L –0.3 m s (in the same direction as
1 2 3
= 500 + 250 + 225 the motion of the bicycle).
= 975 m
Displacement to the left = L
4
= 135 m
Total displacement = L + L + L + L
1 2 3 4
= 500 + 250 + 225 + (–135)
= 840 m to the right
Figure 2.21 Linear motion of a bicycle
Average speed and average velocity can be determined from the rate of change of the total
distance and also from the rate of change of the total displacement. Try to determine the average
speed and average velocity for the velocity-time graph above.
39
2.2.3
2.2.3 39