Page 464 - (DK) The Ultimate Visual Dictionary 2nd Ed.
P. 464
ARCHITECTURE
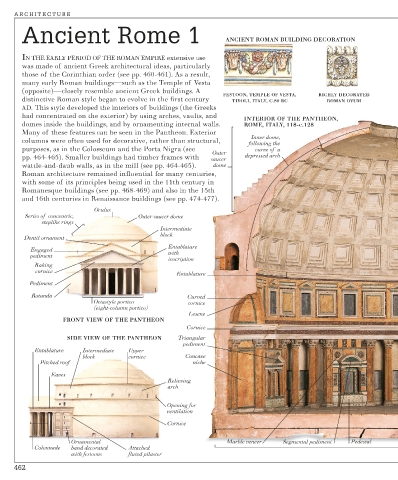
Ancient Rome 1 ANCIENT ROMAN BUILDING DECORATION
IN THE EARLY PERIOD OF THE ROMAN EMPIRE extensive use
was made of ancient Greek architectural ideas, particularly
those of the Corinthian order (see pp. 460-461). As a result,
many early Roman buildings—such as the Temple of Vesta
(opposite)—closely resemble ancient Greek buildings. A
FESTOON, TEMPLE OF VESTA, RICHLY DECORATED
distinctive Roman style began to evolve in the first century TIVOLI, ITALY, C.80 BC ROMAN OVUM
AD. This style developed the interiors of buildings (the Greeks
had concentrated on the exterior) by using arches, vaults, and
INTERIOR OF THE PANTHEON,
domes inside the buildings, and by ornamenting internal walls. ROME, ITALY, 118-c.128
Many of these features can be seen in the Pantheon. Exterior
Inner dome,
columns were often used for decorative, rather than structural,
following the
purposes, as in the Colosseum and the Porta Nigra (see curve of a
Outer
pp. 464-465). Smaller buildings had timber frames with saucer depressed arch
wattle-and-daub walls, as in the mill (see pp. 464-465). dome
Roman architecture remained influential for many centuries,
with some of its principles being used in the 11th century in
Romanesque buildings (see pp. 468-469) and also in the 15th
and 16th centuries in Renaissance buildings (see pp. 474-477).
Oculus
Series of concentric, Outer saucer dome
steplike rings
Intermediate
block
Dentil ornament
Entablature
Engaged with
pediment
inscription
Raking
cornice
Entablature
Pediment
Rotunda Curved
Octastyle portico cornice
(eight-column portico)
Lesene
FRONT VIEW OF THE PANTHEON
Cornice
SIDE VIEW OF THE PANTHEON Triangular
pediment
Entablature Intermediate Upper
block cornice Concave
Pitched roof niche
Eaves
Relieving
arch
Opening for
ventilation
Cornice
Ornamental Marble veneer Segmental pediment Pedestal
Colonnade band decorated Attached
with festoons fluted pilaster
462