Page 55 - How It Works - Book of Amazing Answers To Curious Questions, 12
P. 55
Environment Q�
_______________
Why are geysers �n rare?
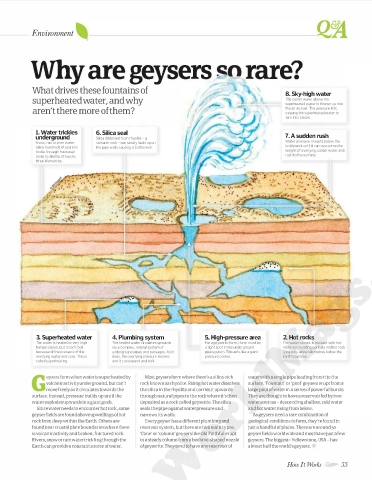
What drives these fountains of 8. Sky-high water
superheated water, and why The colder water above the
superheated water is thrown up into
aren't there more of them? the air as a jet. The pressure lifts,
causing the superheated water to
turn into steam.
1. Water trickles 6. Silica seal
underground Silica dissolved from rhyolite - a 7. A sudden rush
Snow, rain or river water volcanic rock - can slowly build up on Water pressure mounts below the
takes hundreds of years to the pipe walls causing a bottleneck. bottleneck until it can overcome the
trickle through fractured weight of overlying, colder water and
rocks to depths of two to rush to the surface.
three kilometres.
• . • • ;': . 4 •• :
..
3. Superheated water 4. Plumbing system 5. High-pressure area 2. Hot rocks
The water is heated to very high The heated water circulates upwards For a geyser to form, there must be The water comes in contact with hot
temperatures, but it can't boil via a complex, natural system of a tight spot in the underground rocks surrounding partially molten rock
because of the pressure of the underground pipes and passages. As it pipe system. This acts like a giant lying only a few kilometres below the
overlying water and rock. This is does, the overlying pressure lessens pressure cooker. Earth's surface.
called superheating. and it can expand and boil.
eysers form when water is superheated by Most geysers form where there's a silica-rich water with a single pipe leading from it to the
volcanic activity underground, but can't rock known as rhyolite. Rising hot water dissolves surface. 'Fountain' or 'pool' geysers erupt from a
G move freely as it circulates towards the the silica in the rhyolite and carries it upwards large pool of water in a series of powerful bursts.
surface. Instead, pressure builds up until the through natural pipes in the rock where it's then They are thought to have a reservoir fed by two
water explodes upwards in a giant gush. deposited as a rock called geyserite. The silica water sources- descending shallow, cold water
Since water needs to encounter hot rock, some seals the pipe against water pressure and and hot water rising from below.
geyser fields are found above upwellings of hot narrows its walls. As geysers need a rare combination of
rock from deep within the Earth. Others are Every geyser has a different plumbing and geological conditions to form, they're found in
found near crustal plate boundaries where there reservoir system, but there are two main types. just a handful of places. There are around 50
is volcanic activity and broken, fractured rock. 'Cone' or 'column' geysers like Old Faithful erupt geyser fields worldwide and most have just a few
Rivers, snow or rainwater trick! ing through the in a steady column from a beehive-shaped nozzle geysers. The biggest- Yellowstone, USA-has
Earth can provide a constant source of water. of geyserite. They tend to have one reservoir of almost half the world's geysers.
WorldMags.net
WorldMags.net How It T%rks 55