Page 69 - How It Works - Book of Amazing Answers To Curious Questions, 12
P. 69
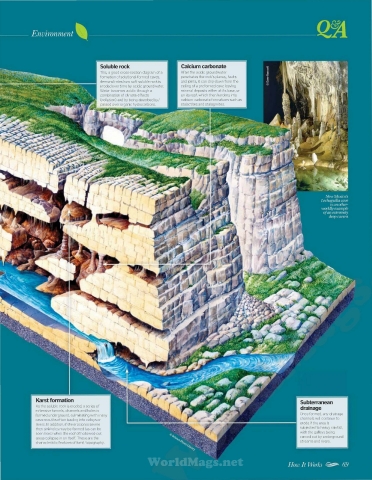
This, a good cross-section diagram of a After the acidic groundwater
formation of solutional-formed caves, penetrates the rock's planes, faults
demonstrates how soft soluble rock is and joints, it can drip down from the
eroded over time by acidic groundwater. ceiling of a preformed cave leaving
Water becomes acidic through a mineral deposits either at its base, or
combination of climate effects on its roof, which then hardens into
(pollution) and by being absorbed by/ calcium carbonate formations such as
passed over organic hydrocarbons. stalactites and stalagmites.
As the soluble rock is eroded, a series of
extensive tunnels, channels and holes is
formed underground, culminating with many Once formed, any drainage
cave mouths often leading into valleys or channels will continue to
rivers. In addition, if the erosion is severe erode if the area is
then sinkholes may be formed (as can be subjected to heavy rainfall,
seen here) when the roof of hollowed-out with the gulleys being
areas collapse in on itself. These are the carved out by underground
characteristic features of karst topography. streams and rivers.
WorldMags.net
WorldMags.net