Page 72 - (DK) Help Your Kids with Language Arts
P. 72
70 GRAMMAR
Compound sentences SEE ALSO
58–59 Conjunctions
A COMPOUND SENTENCE IS A SENTENCE THAT HAS MORE 66–67 Clauses
68–69 Sentences
THAN ONE MAIN CLAUSE. Complex sentences 72–73
Semicolons 100–101
Compound sentences are made up of two or more main clauses,
Colons 102–103
but no subordinate clauses. The main clauses are linked using
conjunctions, and the resulting sentence conveys different
ideas of equal importance.
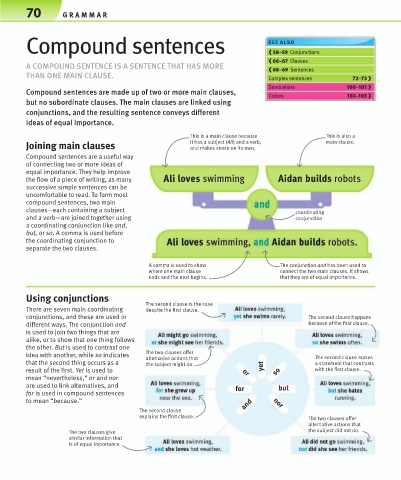
This is a main clause because This is also a
Joining main clauses it has a subject (Ali) and a verb, main clause.
and makes sense on its own.
Compound sentences are a useful way
of connecting two or more ideas of
equal importance. They help improve
the flow of a piece of writing, as many Ali loves swimming Aidan builds robots
successive simple sentences can be
uncomfortable to read. To form most
compound sentences, two main
clauses—each containing a subject coordinating
and a verb—are joined together using conjunction
a coordinating conjunction like and,
but, or so. A comma is used before
the coordinating conjunction to
separate the two clauses.
A comma is used to show The conjunction and has been used to
where one main clause connect the two main clauses. It shows
ends and the next begins. that they are of equal importance.
Using conjunctions
The second clause is the case
There are seven main coordinating despite the first clause.
conjunctions, and these are used in The second clause happens
different ways. The conjunction and because of the first clause.
is used to join two things that are
alike, or to show that one thing follows
the other. But is used to contrast one
The two clauses offer
idea with another, while so indicates alternative actions that The second clause makes
that the second thing occurs as a the subject might do. yet a statement that contrasts
result of the first. Yet is used to or so with the first clause.
mean “nevertheless,” or and nor
are used to link alternatives, and for but
for is used in compound sentences
to mean “because.” and nor
The second clause
explains the first clause.
The two clauses offer
alternative actions that
The two clauses give the subject did not do.
similar information that
is of equal importance.