Page 63 - Fish and Amphibians (Britannica Illustrated Science Library)
P. 63
58 DIVERSITY FISH AND AMPHIBIANS 59
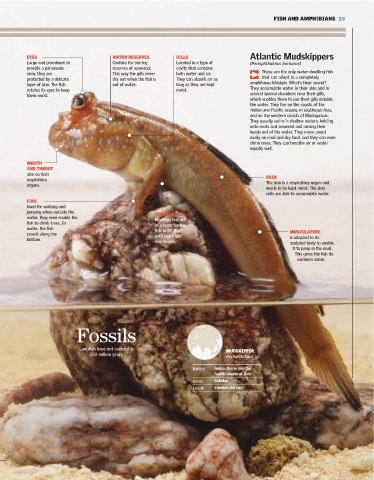
Out of the Water EYES WATER RESERVES GILLS Atlantic Mudskippers
Large and prominent to Cavities for storing Located in a type of (Periophthalmus barbarus)
provide a panoramic reserves of seawater. cavity that contains
ome species of fish can breathe and live out of the water. They include the mudskippers view, they are This way the gills never both water and air. These are the only water-dwelling fish
that can adapt to a completely
protected by a delicate dry out when the fish is They can absorb air as
in southeast Asia, which can stay on muddy flats and even climb trees. To breathe, they layer of skin. The fish out of water.. long as they are kept amphibious lifestyle. What's their secret?
S need only their skin to stay moist, thanks to the function of certain cells in their skin. A rotates its eyes to keep moist. They accumulate water in their skin and in
several special chambers near their gills,
them moist.
few other species still have rudimentary lungs like those of the first aquatic animals that which enables them to use their gills outside
the water. They live on the coasts of the
colonized dry land. Indian and Pacific oceans, in southeast Asia,
and on the western coasts of Madagascar.
They usually swim in shallow waters, holding
onto roots and seaweed and raising their
heads out of the water. They move about
easily on mud and dry land, and they can even
Fish with Lungs climb trees. They can breathe air or water
SOUTH AMERICAN LUNGFISH equally well.
Lungfish have rudimentary lungs that Lepidosiren paradoxa
originate from a connection between the
swim bladder and the esophagus. This allows has a small gill apparatus and two MOUTH
lungs with which it breathes during
the swim bladder to function using air when the the dry season.. AND THROAT
fish leaves the water. Depending on the species, also contain
the fish can breathe air occasionally or even respiratory SKIN
indefinitely. Many varieties of these fish have WEST AFRICAN LUNGFISH organs. The skin is a respiratory organ and
been found in fossil form all over the world, Protopterus annectens annectens needs to be kept moist. The skin
which indicates that they were very widespread has fleshy fins that look like limbs cells are able to accumulate water.
during the Mesozoic Era. They were probably and three external gills. In the dry FINS
the first vertebrates to develop lungs. However, season it secretes a substance for Used for walking and
lungfish species are found in only three areas covering itself. It can remain in this jumping when outside the VENTRAL DISK
today, all in freshwater environments. state for up to a year. water, they even enable the Modified fins act
fish to climb trees. In as a lever for the
water, the fish
fish to lift itself MUSCULATURE
crawls along the
9 months QUEENSLAND LUNGFISH bottom. onto roots and is adapted to its
tree trunks.
sculpted body to enable
Neoceratodus forsteri
When forced to breathe air for long it to jump in the mud.
Length of time certain This gives the fish its
periods, this fish will die. It can
lungfish can live buried in reach up to 50 inches (1.25 m) long, common name.
the mud weigh 22 pounds (10 kg), and live
more than 65 years..
1 WATER LEVELS DROP 2 HEAD FIRST 3 TURNING AROUND 4 HIBERNATION
The fish looks for an area On entering the burrow head The lungfish curls in on itself The fish breathes through
with soft mud under the first, the fish secretes thick with its head up. Before the two or three small holes in
water, where it can easily mucus, which enables it to slide water level drops, it seals the the plug. Its bodily functions
dig itself a burrow. in easily and also protects it entry with a plug of clay. are reduced to a minimum.
from dehydration.
Fossils
Lungfish have not evolved in
Some water is still 250 million years. MUDSKIPPER
left in the pond. The water Periophtalmus sp.
has receded
completely.
Habitat Indian Ocean and the
Pacific coasts of Asia
Family Gobidae
Length 6 inches (15 cm)
In the Mud Mud Mud
When the dry season arrives, and rivers and
ponds dry up, both the African and South
American species of lungfish dig holes in the mud
along the shore and bury themselves. They then reduce
their metabolic functions to a minimum and burn as
little energy as possible until the waters rise again.