Page 67 - Fish and Amphibians (Britannica Illustrated Science Library)
P. 67
62 AMPHIBIANS FISH AND AMPHIBIANS 63
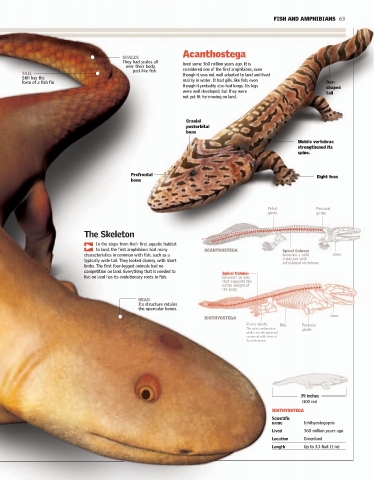
Distant Kin SCALES Acanthostega
They had scales all
over their body, lived some 360 million years ago. It is
just like fish. considered one of the first amphibians, even
he first amphibians evolved from fish with fleshy, lobed fins that resembled legs. TAIL though it was not well adapted to land and lived
Still has the
They may have been attracted to land as a source for food, but the most important form of a fish fin mainly in water. It had gills, like fish, even Oar-
though it probably also had lungs. Its legs
shaped
T reason for their leaving the water was the instability of the Devonian Period, which were well developed, but they were tail
not yet fit for moving on land.
drastically affected freshwater environments. During long droughts, the fish used their
fleshy fins to move from one pond to another. Oxygen availability was also affected, and
this led to more organisms being able to breathe oxygen from the air.
Cranial
postorbital
bone
Mobile vertebrae
Legs: Evolution strengthened its
spine.
In 2004, American paleontologist Neil
Shubin of the University of Chicago
offered the scientific community a complete
description of a humerus bone that was 365 Prefrontal Eight toes
million years old. The first tetrapods adapted bone
to land exhibited a great variety of leg
GLYPTOTEPIS
shapes, sizes, and strengths. After
comparing this fossil with that of other
tetrapods, scientists concluded that the Rays of skin
evolution of the legs and of the muscles Pelvic Pectoral
necessary for walking began in the girdle girdle
water.
Ulna
The Skeleton
Tiktaalik EUSTHENOPTERON In the steps from their first aquatic habitat
Radius Humerus to land, the first amphibians had many ACANTHOSTEGA Spinal Column
A lobe-finned fish from the late characteristics in common with fish, such as a becomes a solid Jaws
Devonian Period, with many tetrapod structure with
typically wide tail. They looked clumsy, with short
characteristics. It lived 375 million articulated vertebrae.
Rays of skin limbs. The first four-legged animals had no
years ago. Some paleontologists suggest
competition on land. Everything that is needed to
that it was another intermediate form live on land has its evolutionary roots in fish. Spinal Column
between fish and amphibians. Ulna becomes an axis
that supports the
PANDERICHTHYS entire weight of
the body.
Humerus
HEAD
Its structure retains
Radius the opercular bones.
Humerus
ICHTHYOSTEGA Jaws
Pelvic Girdle Ribs Pectoral
Ulna The pelvic and pectoral girdle
girdles are strengthened
ACANTHOSTEGA compared with those of
its predecessor.
Eusthenopteron
Radius
A relatively large fish, about 29 inches (75 cm) long.
ICHTHYOSTEGA
Many features of its skeleton were similar to those of
the first amphibians; it had a cranial pattern similar
to Acanthostega and Ichtyostega. The skeleton of its
fins included a humerus, ulna, and radius in the front Humerus
fin and a femur, tibia, and fibula in the pelvic fin.
39 inches
(100 cm)
Ulna Radius
ICHTHYOSTEGA
Scientific
name Ichthyostegopsis
Lived 360 million years ago
Seven LEGS
toes There are Location Greenland
Three-lobed tail Pelvic fin Muscled pectoral fin
seven toes on Length Up to 3.3 feet (1 m)
each hind leg.