Page 72 - Fish and Amphibians (Britannica Illustrated Science Library)
P. 72
68 AMPHIBIANS FISH AND AMPHIBIANS 69
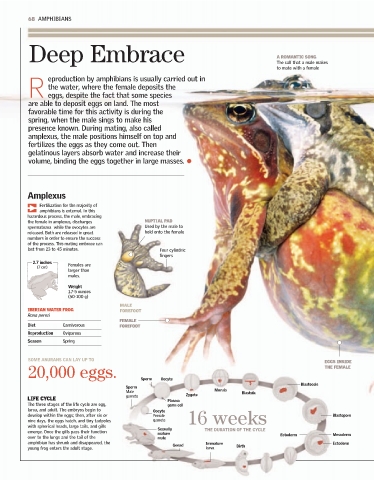
Deep Embrace A ROMANTIC SONG Responsible Parents EUROPEAN MIDWIFE TOAD 35-60
The call that a male makes Some males of frog and toad species play Alytes obstetricans
The male winds up the string of eggs that the
to mate with a female an important role in the protection of the female has laid over his hind legs. He carries THE NUMBER OF EGGS THE
eggs laid by the female. They pick up the eggs the eggs for a month, provides them with a TOAD CAN CARRY ON HIS BACK
eproduction by amphibians is usually carried out in and help the mothers, and some even carry the moist environment, and leaves them in the
eggs with them until the birth takes place.
the water, where the female deposits the water so the young can swim away.
R eggs, despite the fact that some species
Inside of
are able to deposit eggs on land. The most the egg
favorable time for this activity is during the
spring, when the male sings to make his
presence known. During mating, also called
amplexus, the male positions himself on top and
fertilizes the eggs as they come out. Then THE MALE
gelatinous layers absorb water and increase their holds the female and
deposits the sperm.
volume, binding the eggs together in large masses.
The tadpoles
are born in
the water.
Amplexus
Fertilization for the majority of
amphibians is external. In this
hazardous process, the male, embracing
the female in amplexus, discharges NUPTIAL PAD
spermatozoa while the ovocytes are Used by the male to
released. Both are released in great hold onto the female SURINAM TOAD The young are identical
numbers in order to ensure the success Pipa pipa to their parents.
of the process. This mating embrace can The female goes around in circles,
last from 23 to 45 minutes. Four cylindric releasing one egg each time. The
fingers male places the egg on the Hatching
2.7 inches Females are female's back, and she covers egg
(7 cm) them with her swollen skin to
larger than protect them until they hatch.
males.
Weight Release of
1.7-5 ounces THE FEMALE the tadpoles
(50-100 g) lays the eggs in a string.
MALE
IBERIAN WATER FROG FOREFOOT
Rana perezi
FEMALE
Diet Carnivorous FOREFOOT
Reproduction Oviparous
Season Spring
The tadpoles
absorb oxygen.
SOME ANURANS CAN LAY UP TO
EGGS INSIDE
20,000 eggs. THE FEMALE HINDFEET
Sperm Oocyte
Blastocele
Sperm
Male Morula Blastula
gamete Zygote
LIFE CYCLE
Plasma
The three stages of the life cycle are egg, germ cell
larva, and adult. The embryos begin to Oocyte
develop within the eggs; then, after six or Female Blastopore
nine days, the eggs hatch, and tiny tadpoles gamete 16 weeks
with spherical heads, large tails, and gills
Sexually THE DURATION OF THE CYCLE
emerge. Once the gills pass their function mature Mesoderm
over to the lungs and the tail of the male Ectoderm
amphibian has shrunk and disappeared, the Immature Ectoderm
Gonad Birth
young frog enters the adult stage. larva