Page 69 - How It Works - Book Of Amazing Answers To Curious Questions, Volume 05-15
P. 69
Science
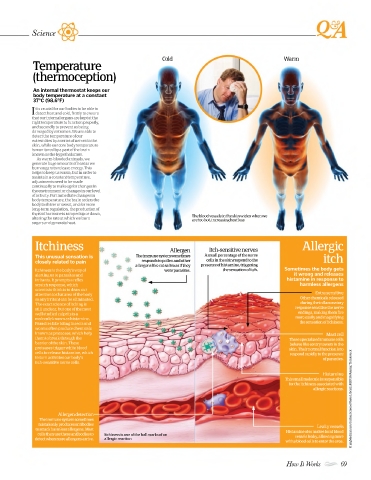
Cold Warm
Temperature
(thermoception)
An internal thermostat keeps our
body temperature at a constant
37°C (98.6°F)
t is crucial for our bodies to be able to
Idetect heat and cold, firstly to ensure
that our internal organs are kept at the
right temperature to function properly,
and secondly to prevent us being
damaged by extremes. We are able to
detect the temperature of our
extremities by a series of nerves in the
skin, while our core body temperature
is monitored by a part of the brain
known as the hypothalamus.
As warm-blooded animals, we
generate huge amounts of heat as we
burn sugars to release energy. This
helps to keep us warm, but in order to
maintain a constant temperature,
adjustments need to be made
continually to make up for changes in
the environment or changes in our level
of activity. For immediate changes in
body temperature, the brain orders the
body to shiver or sweat, and for more
long-term regulation, the production of
thyroid hormone is ramped up or down, The blood vessels in the skin widen when we
altering the rate at which we burn are too hot, increasing heat loss
sugars and generate heat.
Itchiness Allergen Itch-sensitive nerves Allergic
This unusual sensation is The immune system sometimes A small percentage of the nerve itch
closely related to pain responds to pollen and other cells in the skin respond to the
allergens like cat saliva as if they presence of histamine, triggering
Itchiness is the body’s way of were parasites. the sensation of itch. Sometimes the body gets
alerting us to parasites and it wrong and releases
irritants. It prompts a refl ex histamine in response to
scratch response, which harmless allergens
scientists think is to draw our
attention to that area of the body Extra sensitive
so any irritant can be eliminated. Other chemicals released
The exact science of itching is during the inflammatory
still unclear, but one of the most response sensitise the nerve
well studied culprits is a endings, making them fire
molecule known as histamine. more easily and magnifying
Parasites like biting insects and the sensation of itchiness.
worms often produce chemicals
known as proteases, which help Mast cell
them to break through the These specialised immune cells
barrier of the skin. These behave like sentry towers in the
proteases trigger white blood skin. Their normal function is to
cells to release histamine, which respond rapidly to the presence
in turn activates our body’s of parasites.
itch-sensitive nerve cells.
Histamine
This small molecule is responsible
for the itchiness associated with
allergic reactions. © 3d4Medical.com/Corbis; Science Photo Library; BSIP SA/Alamy; Thinkstock
Allergen detection
The immune system sometimes
mistakenly produces antibodies
Leaky vessels
to attack harmless allergens. Mast Histamine also makes local blood
cells then use these antibodies to Itchiness is one of the hallmarks of an
detect when more allergens arrive. allergic reaction vessels leaky, allowing more
white blood cells to enter the area.
How It Works 69