Page 15 - REC :: M.E. CS Curriculum and Syllabus - R2019
P. 15
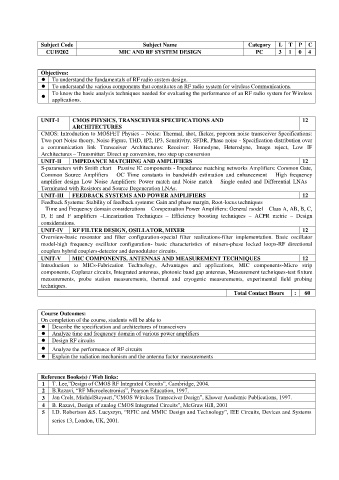
Subject Code Subject Name Category L T P C
CU19202 MIC AND RF SYSTEM DESIGN PC 3 1 0 4
Objectives:
To understand the fundamentals of RF radio system design.
To understand the various components that constitutes an RF radio system for wireless Communications.
To know the basic analysis techniques needed for evaluating the performance of an RF radio system for Wireless
applications.
UNIT-I CMOS PHYSICS, TRANSCEIVER SPECIFICATIONS AND 12
ARCHITECTURES
CMOS: Introduction to MOSFET Physics – Noise: Thermal, shot, flicker, popcorn noise transceiver Specifications:
Two port Noise theory, Noise Figure, THD, IP2, IP3, Sensitivity, SFDR, Phase noise - Specification distribution over
a communication link Transceiver Architectures: Receiver: Homodyne, Heterodyne, Image reject, Low IF
Architectures – Transmitter: Direct up conversion, two step up conversion
UNIT-II IMPEDANCE MATCHING AND AMPLIFIERS 12
S-parameters with Smith chart – Passive IC components - Impedance matching networks Amplifiers: Common Gate,
Common Source Amplifiers – OC Time constants in bandwidth estimation and enhancement – High frequency
amplifier design Low Noise Amplifiers: Power match and Noise match – Single ended and Differential LNAs –
Terminated with Resistors and Source Degeneration LNAs.
UNIT-III FEEDBACK SYSTEMS AND POWER AMPLIFIERS 12
Feedback Systems: Stability of feedback systems: Gain and phase margin, Root-locus techniques
– Time and Frequency domain considerations – Compensation Power Amplifiers: General model – Class A, AB, B, C,
D, E and F amplifiers –Linearization Techniques – Efficiency boosting techniques – ACPR metric – Design
considerations.
UNIT-IV RF FILTER DESIGN, OSILLATOR, MIXER 12
Overview-basic resonator and filter configuration-special filter realizations-filter implementation. Basic oscillator
model-high frequency oscillator configuration- basic characteristics of mixers-phase locked loops-RF directional
couplers hybrid couplers-detector and demodulator circuits.
UNIT-V MIC COMPONENTS, ANTENNAS AND MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUES 12
Introduction to MICs-Fabrication Technology, Advantages and applications, MIC components-Micro strip
components, Coplanar circuits, Integrated antennas, photonic band gap antennas, Measurement techniques-test fixture
measurements, probe station measurements, thermal and cryogenic measurements, experimental field probing
techniques.
Total Contact Hours : 60
Course Outcomes:
On completion of the course, students will be able to
Describe the specification and architectures of transceivers
Analyze time and frequency domain of various power amplifiers
Design RF circuits
Analyze the performance of RF circuits
Explain the radiation mechanism and the antenna factor measurements
Reference Books(s) / Web links:
1 T. Lee,”Design of CMOS RF Integrated Circuits”, Cambridge, 2004.
2 B.Razavi, “RF Microelectronics”, Pearson Education, 1997.
3 Jan Crols, MichielSteyaert,”CMOS Wireless Transceiver Design”, Kluwer Academic Publications, 1997.
4 B. Razavi, Design of analog CMOS Integrated Circuits”, McGraw Hill, 2001
5 I.D. Robertson &S. Lucyszyn, “RFIC and MMIC Design and Technology”, IEE Circuits, Devices and Systems
series 13, London, UK, 2001.