Page 15 - REC :: B.E. EEE Curriculum and Syllabus - R2019
P. 15
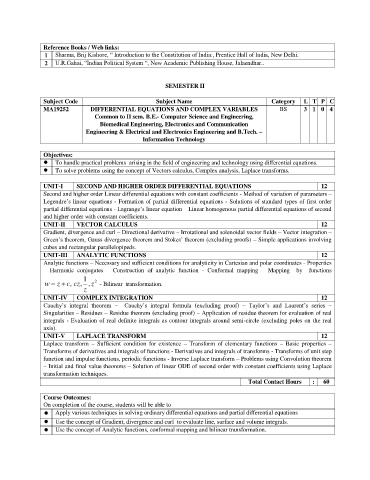
Reference Books / Web links:
1 Sharma, Brij Kishore, “ Introduction to the Constitution of India:, Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi.
2 U.R.Gahai, “Indian Political System “, New Academic Publishing House, Jalaendhar..
SEMESTER II
Subject Code Subject Name Category L T P C
MA19252 DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS AND COMPLEX VARIABLES BS 3 1 0 4
Common to II sem. B.E.- Computer Science and Engineering,
Biomedical Engineering, Electronics and Communication
Engineering & Electrical and Electronics Engineering and B.Tech. –
Information Technology
Objectives:
To handle practical problems arising in the field of engineering and technology using differential equations.
To solve problems using the concept of Vectors calculus, Complex analysis, Laplace transforms.
UNIT-I SECOND AND HIGHER ORDER DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS 12
Second and higher order Linear differential equations with constant coefficients - Method of variation of parameters –
Legendre’s linear equations - Formation of partial differential equations - Solutions of standard types of first order
partial differential equations - Lagrange’s linear equation – Linear homogenous partial differential equations of second
and higher order with constant coefficients.
UNIT-II VECTOR CALCULUS 12
Gradient, divergence and curl – Directional derivative – Irrotational and solenoidal vector fields – Vector integration –
Green’s theorem, Gauss divergence theorem and Stokes’ theorem (excluding proofs) – Simple applications involving
cubes and rectangular parallelopipeds.
UNIT-III ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS 12
Analytic functions – Necessary and sufficient conditions for analyticity in Cartesian and polar coordinates - Properties
– Harmonic conjugates – Construction of analytic function - Conformal mapping – Mapping by functions
1
w z , c cz , , z - Bilinear transformation.
2
z
UNIT-IV COMPLEX INTEGRATION 12
Cauchy’s integral theorem – Cauchy’s integral formula (excluding proof) – Taylor’s and Laurent’s series –
Singularities – Residues – Residue theorem (excluding proof) – Application of residue theorem for evaluation of real
integrals - Evaluation of real definite integrals as contour integrals around semi-circle (excluding poles on the real
axis).
UNIT-V LAPLACE TRANSFORM 12
Laplace transform – Sufficient condition for existence – Transform of elementary functions – Basic properties –
Transforms of derivatives and integrals of functions - Derivatives and integrals of transforms - Transforms of unit step
function and impulse functions, periodic functions - Inverse Laplace transform – Problems using Convolution theorem
– Initial and final value theorems – Solution of linear ODE of second order with constant coefficients using Laplace
transformation techniques.
Total Contact Hours : 60
Course Outcomes:
On completion of the course, students will be able to
Apply various techniques in solving ordinary differential equations and partial differential equations
Use the concept of Gradient, divergence and curl to evaluate line, surface and volume integrals.
Use the concept of Analytic functions, conformal mapping and bilinear transformation.