Page 116 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 116
72 SECTION II BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—METABOlISM BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—METABOlISM
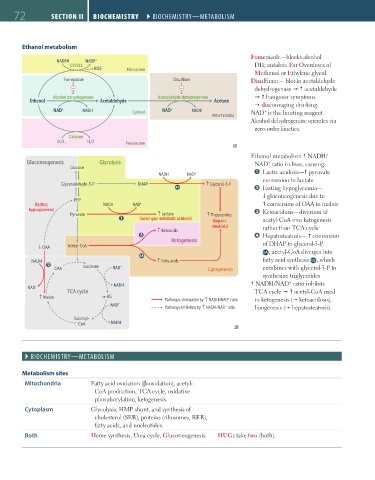
Ethanol metabolism
Fomepizole—blocks alcohol
NADPH NADP +
CYP2E1 DH; antidote For Overdoses of
ROS Microsome
Methanol or Ethylene glycol.
Fomepizole Disulfiram Disulfiram— blocks acetaldehyde
– – dehydrogenase acetaldehyde
Alcohol dehydrogenase Acetaldehyde dehydrogenase hangover symptoms
Ethanol Acetaldehyde Acetate
discouraging drinking.
NAD + NADH Cytosol NAD + NADH NAD is the limiting reagent.
+
Mitochondria
Alcohol dehydrogenase operates via
zero-order kinetics.
Catalase
H O H O
2 2 2 Peroxisome
Ethanol metabolism NADH/
Gluconeogenesis Glycolysis NAD ratio in liver, causing:
+
Glucose
NADH NAD + Lactic acidosis— pyruvate
conversion to lactate
Glyceraldehyde-3-P DHAP ↑ Glycerol-3-P
4 A Fasting hypoglycemia—
gluconeogenesis due to
PEP
(fasting NADH NAD + conversion of OAA to malate
hypoglycemia) Ketoacidosis—diversion of
Pyruvate ↑ Lactate ↑ Triglycerides
Q (anion gap metabolic acidosis)
(hepatic acetyl-CoA into ketogenesis
steatosis) rather than TCA cycle
↑ Ketoacids
S Hepatosteatosis— conversion
Ketogenesis of DHAP to glycerol-3-P
OAA Acetyl-CoA
4A ; acetyl-CoA diverges into
↑
4 B
NADH ↑ Fatty acids fatty acid synthesis 4B , which
R Isocitrate +
OAA NAD Lipogenesis combines with glycerol-3-P to
synthesize triglycerides
+
NAD + NADH NADH/NAD ratio inhibits
TCA cycle TCA cycle acetyl-CoA used
↑ Malate α-KG +
Pathways stimulated by ↑ NADH/NAD ratio in ketogenesis ( ketoacidosis),
NAD + +
Pathways inhibited by ↑ NADH/NAD ratio lipogenesis ( hepatosteatosis).
Succinyl-
CoA NADH
` `BIOCHEMISTRY—METABOlISM
Metabolism sites
Mitochondria Fatty acid oxidation (β-oxidation), acetyl-
CoA production, TCA cycle, oxidative
phosphorylation, ketogenesis.
Cytoplasm Glycolysis, HMP shunt, and synthesis of
cholesterol (SER), proteins (ribosomes, RER),
fatty acids, and nucleotides.
Both Heme synthesis, Urea cycle, Gluconeogenesis. HUGs take two (both).
FAS1_2019_01-Biochem.indd 72 11/7/19 3:16 PM