Page 117 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 117
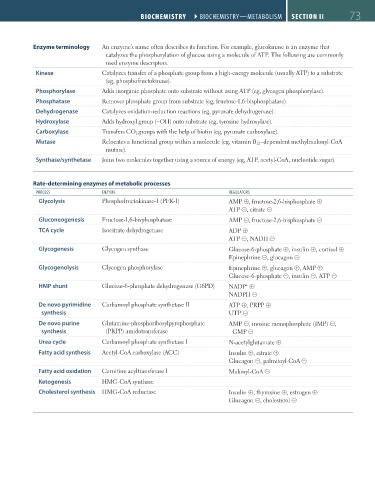
BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—METABOlISM BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—METABOlISM SECTION II 73
Enzyme terminology An enzyme’s name often describes its function. For example, glucokinase is an enzyme that
catalyzes the phosphorylation of glucose using a molecule of ATP. The following are commonly
used enzyme descriptors.
Kinase Catalyzes transfer of a phosphate group from a high-energy molecule (usually ATP) to a substrate
(eg, phosphofructokinase).
Phosphorylase Adds inorganic phosphate onto substrate without using ATP (eg, glycogen phosphorylase).
Phosphatase Removes phosphate group from substrate (eg, fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase).
Dehydrogenase Catalyzes oxidation-reduction reactions (eg, pyruvate dehydrogenase).
Hydroxylase Adds hydroxyl group (−OH) onto substrate (eg, tyrosine hydroxylase).
Carboxylase Transfers CO 2 groups with the help of biotin (eg, pyruvate carboxylase).
Mutase Relocates a functional group within a molecule (eg, vitamin B 12 –dependent methylmalonyl-CoA
mutase).
Synthase/synthetase Joins two molecules together using a source of energy (eg, ATP, acetyl-CoA, nucleotide sugar).
Rate-determining enzymes of metabolic processes
PROCESS ENZYME REGUlATORS
Glycolysis Phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1) AMP ⊕, fructose-2,6-bisphosphate ⊕
ATP ⊝, citrate ⊝
Gluconeogenesis Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase AMP ⊝, fructose-2,6-bisphosphate ⊝
TCA cycle Isocitrate dehydrogenase ADP ⊕
ATP ⊝, NADH ⊝
Glycogenesis Glycogen synthase Glucose-6-phosphate ⊕, insulin ⊕, cortisol ⊕
Epinephrine ⊝, glucagon ⊝
Glycogenolysis Glycogen phosphorylase Epinephrine ⊕, glucagon ⊕, AMP ⊕
Glucose-6-phosphate ⊝, insulin ⊝, ATP ⊝
HMP shunt Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) NADP ⊕
+
NADPH ⊝
De novo pyrimidine Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II ATP ⊕, PRPP ⊕
synthesis UTP ⊝
De novo purine Glutamine-phosphoribosylpyrophosphate AMP ⊝, inosine monophosphate (IMP) ⊝,
synthesis (PRPP) amidotransferase GMP ⊝
Urea cycle Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I N-acetylglutamate ⊕
Fatty acid synthesis Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) Insulin ⊕, citrate ⊕
Glucagon ⊝, palmitoyl-CoA ⊝
Fatty acid oxidation Carnitine acyltransferase I Malonyl-CoA ⊝
Ketogenesis HMG-CoA synthase
Cholesterol synthesis HMG-CoA reductase Insulin ⊕, thyroxine ⊕, estrogen ⊕
Glucagon ⊝, cholesterol ⊝
FAS1_2019_01-Biochem.indd 73 11/7/19 3:16 PM