Page 119 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 119
BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—METABOlISM BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—METABOlISM SECTION II 75
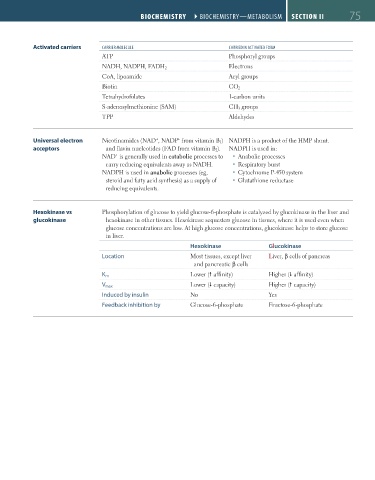
Activated carriers CARRIER MOlECUlE CARRIED IN ACTIVATED FORM
ATP Phosphoryl groups
Electrons
NADH, NADPH, FADH 2
CoA, lipoamide Acyl groups
Biotin CO 2
Tetrahydrofolates 1-carbon units
S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) CH 3 groups
TPP Aldehydes
Universal electron Nicotinamides (NAD , NADP from vitamin B 3 ) NADPH is a product of the HMP shunt.
+
+
acceptors and flavin nucleotides (FAD from vitamin B 2 ). NADPH is used in:
+
NAD is generally used in catabolic processes to Anabolic processes
carry reducing equivalents away as NADH. Respiratory burst
NADPH is used in anabolic processes (eg, Cytochrome P-450 system
steroid and fatty acid synthesis) as a supply of Glutathione reductase
reducing equivalents.
Hexokinase vs Phosphorylation of glucose to yield glucose-6-phosphate is catalyzed by glucokinase in the liver and
glucokinase hexokinase in other tissues. Hexokinase sequesters glucose in tissues, where it is used even when
glucose concentrations are low. At high glucose concentrations, glucokinase helps to store glucose
in liver.
Hexokinase Glucokinase
Location Most tissues, except liver Liver, β cells of pancreas
and pancreatic β cells
Lower ( affinity) Higher ( affinity)
K m
V max Lower ( capacity) Higher ( capacity)
Induced by insulin No Yes
Feedback inhibition by Glucose-6-phosphate Fructose-6-phosphate
FAS1_2019_01-Biochem.indd 75 11/7/19 3:16 PM