Page 111 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 111
BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—NUTRITION BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—NUTRITION SECTION II 67
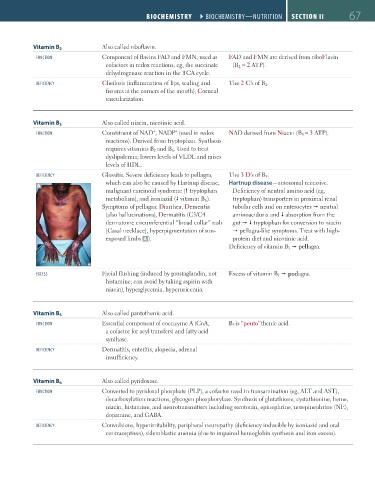
Also called riboflavin.
Vitamin B 2
FUNCTION Component of flavins FAD and FMN, used as FAD and FMN are derived from riboFlavin
cofactors in redox reactions, eg, the succinate (B 2 ≈ 2 ATP).
dehydrogenase reaction in the TCA cycle.
DEFICIENCY Cheilosis (inflammation of lips, scaling and The 2 C’s of B 2 .
fissures at the corners of the mouth), Corneal
vascularization.
Vitamin B 3 Also called niacin, nicotinic acid.
+
+
FUNCTION Constituent of NAD , NADP (used in redox NAD derived from Niacin (B 3 ≈ 3 ATP).
reactions). Derived from tryptophan. Synthesis
requires vitamins B 2 and B 6 . Used to treat
dyslipidemia; lowers levels of VLDL and raises
levels of HDL.
DEFICIENCY Glossitis. Severe deficiency leads to pellagra, The 3 D’s of B 3 .
which can also be caused by Hartnup disease, Hartnup disease—autosomal recessive.
A
malignant carcinoid syndrome ( tryptophan Deficiency of neutral amino acid (eg,
metabolism), and isoniazid ( vitamin B 6 ). tryptophan) transporters in proximal renal
Symptoms of pellagra: Diarrhea, Dementia tubular cells and on enterocytes neutral
(also hallucinations) , Dermatitis (C3/C4 aminoaciduria and absorption from the
dermatome circumferential “broad collar” rash gut tryptophan for conversion to niacin
[Casal necklace], hyperpigmentation of sun- pellagra-like symptoms. Treat with high-
exposed limbs A ). protein diet and nicotinic acid.
Deficiency of vitamin B 3 pellagra.
EXCESS Facial flushing (induced by prostaglandin, not Excess of vitamin B 3 podagra.
histamine; can avoid by taking aspirin with
niacin), hyperglycemia, hyperuricemia.
Vitamin B 5 Also called pantothenic acid.
FUNCTION Essential component of coenzyme A (CoA, B 5 is “pento”thenic acid.
a cofactor for acyl transfers) and fatty acid
synthase.
DEFICIENCY Dermatitis, enteritis, alopecia, adrenal
insufficiency.
Also called pyridoxine.
Vitamin B 6
FUNCTION Converted to pyridoxal phosphate (PLP), a cofactor used in transamination (eg, ALT and AST),
decarboxylation reactions, glycogen phosphorylase. Synthesis of glutathione, cystathionine, heme,
niacin, histamine, and neurotransmitters including serotonin, epinephrine, norepinephrine (NE),
dopamine, and GABA.
DEFICIENCY Convulsions, hyperirritability, peripheral neuropathy (deficiency inducible by isoniazid and oral
contraceptives), sideroblastic anemia (due to impaired hemoglobin synthesis and iron excess).
FAS1_2019_01-Biochem.indd 67 11/7/19 3:16 PM