Page 115 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 115
BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—NUTRITION BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—NUTRITION SECTION II 71
Vitamin K Includes phytomenadione, phylloquinone, phytonadione, menaquinone.
FUNCTION Activated by epoxide reductase to the K is for Koagulation. Necessary for the
reduced form, which is a cofactor for the maturation of clotting factors II, VII, IX,
γ-carboxylation of glutamic acid residues on X, and proteins C and S. Warfarin inhibits
various proteins required for blood clotting. vitamin K–dependent synthesis of these factors
Synthesized by intestinal flora. and proteins.
DEFICIENCY Neonatal hemorrhage with PT and aPTT Not in breast milk; neonates are given vitamin
but normal bleeding time (neonates have K injection at birth to prevent hemorrhagic
sterile intestines and are unable to synthesize disease of the newborn.
vitamin K). Can also occur after prolonged use
of broad-spectrum antibiotics.
Zinc
FUNCTION Mineral essential for the activity of 100+ enzymes. Important in the formation of zinc fingers
(transcription factor motif).
DEFICIENCY Delayed wound healing, suppressed immunity, male hypogonadism, adult hair (axillary, facial,
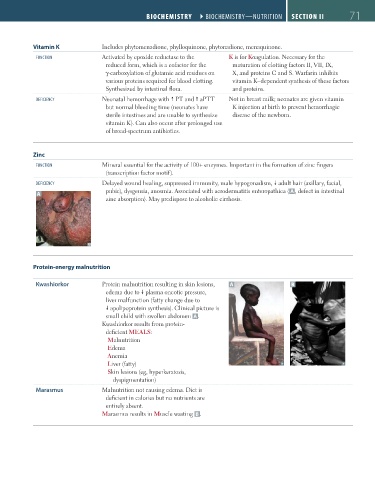
A pubic), dysgeusia, anosmia. Associated with acrodermatitis enteropathica ( A , defect in intestinal
zinc absorption). May predispose to alcoholic cirrhosis.
Protein-energy malnutrition
Kwashiorkor Protein malnutrition resulting in skin lesions, A B
edema due to plasma oncotic pressure,
liver malfunction (fatty change due to
apolipoprotein synthesis). Clinical picture is
small child with swollen abdomen A .
Kwashiorkor results from protein-
deficient MEALS:
Malnutrition
Edema
Anemia
Liver (fatty)
Skin lesions (eg, hyperkeratosis,
dyspigmentation)
Marasmus Malnutrition not causing edema. Diet is
deficient in calories but no nutrients are
entirely absent.
Marasmus results in Muscle wasting B .
FAS1_2019_01-Biochem.indd 71 11/7/19 3:16 PM