Page 122 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 122
78 SECTION II BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—METABOlISM BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—METABOlISM
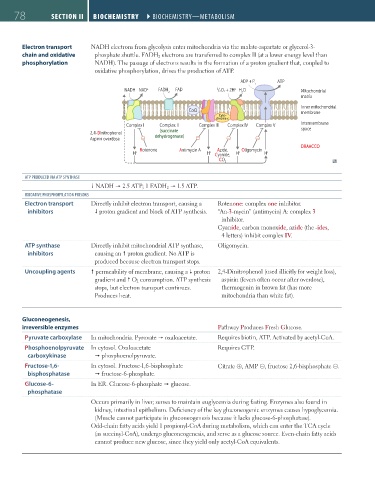
Electron transport NADH electrons from glycolysis enter mitochondria via the malate-aspartate or glycerol-3-
chain and oxidative phosphate shuttle. FADH 2 electrons are transferred to complex II (at a lower energy level than
phosphorylation NADH). The passage of electrons results in the formation of a proton gradient that, coupled to
oxidative phosphorylation, drives the production of ATP.
ADP + P i ATP
+
NADH NAD + FADH 2 FAD 1 / 2O 2 + 2H H O Mitochondrial
2
matrix
Inner mitochondrial
CoQ membrane
Cyto-
chrome c
Complex I Complex II Complex III Complex IV Complex V Intermembrane
space
(succinate
2,4-Dinitrophenol dehydrogenase)
Aspirin overdose
DRAACCO
Rotenone Antimycin A Azide, Oligomycin
H + H + Cyanide, H + H +
CO 2
ATP PRODUCED VIA ATP SYNTHASE
1 NADH 2.5 ATP; 1 FADH 2 1.5 ATP.
OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYlATION POISONS
Electron transport Directly inhibit electron transport, causing a Rotenone: complex one inhibitor.
inhibitors proton gradient and block of ATP synthesis. “An-3-mycin” (antimycin) A: complex 3
inhibitor.
Cyanide, carbon monoxide, azide (the -ides,
4 letters) inhibit complex IV.
ATP synthase Directly inhibit mitochondrial ATP synthase, Oligomycin.
inhibitors causing an proton gradient. No ATP is
produced because electron transport stops.
Uncoupling agents permeability of membrane, causing a proton 2,4-Dinitrophenol (used illicitly for weight loss),
gradient and O 2 consumption. ATP synthesis aspirin (fevers often occur after overdose),
stops, but electron transport continues. thermogenin in brown fat (has more
Produces heat. mitochondria than white fat).
Gluconeogenesis,
irreversible enzymes Pathway Produces Fresh Glucose.
Pyruvate carboxylase In mitochondria. Pyruvate oxaloacetate. Requires biotin, ATP. Activated by acetyl-CoA.
Phosphoenolpyruvate In cytosol. Oxaloacetate Requires GTP.
carboxykinase phosphoenolpyruvate.
Fructose-1,6- In cytosol. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate Citrate ⊕, AMP ⊝, fructose 2,6-bisphosphate ⊝.
bisphosphatase fructose-6-phosphate.
Glucose-6- In ER. Glucose-6-phosphate glucose.
phosphatase
Occurs primarily in liver; serves to maintain euglycemia during fasting. Enzymes also found in
kidney, intestinal epithelium. Deficiency of the key gluconeogenic enzymes causes hypoglycemia.
(Muscle cannot participate in gluconeogenesis because it lacks glucose-6-phosphatase).
Odd-chain fatty acids yield 1 propionyl-CoA during metabolism, which can enter the TCA cycle
(as succinyl-CoA), undergo gluconeogenesis, and serve as a glucose source. Even-chain fatty acids
cannot produce new glucose, since they yield only acetyl-CoA equivalents.
FAS1_2019_01-Biochem.indd 78 11/7/19 3:16 PM