Page 124 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 124
80 SECTION II BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—METABOlISM BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—METABOlISM
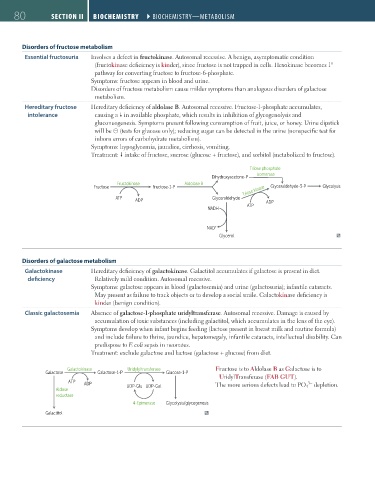
Disorders of fructose metabolism
Essential fructosuria Involves a defect in fructokinase. Autosomal recessive. A benign, asymptomatic condition
(fructokinase deficiency is kinder), since fructose is not trapped in cells. Hexokinase becomes 1°
pathway for converting fructose to fructose-6-phosphate.
Symptoms: fructose appears in blood and urine.
Disorders of fructose metabolism cause milder symptoms than analogous disorders of galactose
metabolism.
Hereditary fructose Hereditary deficiency of aldolase B. Autosomal recessive. Fructose-1-phosphate accumulates,
intolerance causing a in available phosphate, which results in inhibition of glycogenolysis and
gluconeogenesis. Symptoms present following consumption of fruit, juice, or honey. Urine dipstick
will be ⊝ (tests for glucose only); reducing sugar can be detected in the urine (nonspecific test for
inborn errors of carbohydrate metabolism).
Symptoms: hypoglycemia, jaundice, cirrhosis, vomiting.
Treatment: intake of fructose, sucrose (glucose + fructose), and sorbitol (metabolized to fructose).
Triose phosphate
isomerase
Dihydroxyacetone-P
Fructokinase Aldolase B
Fructose Fructose-1-P Triose kinase Glyceraldehyde-3-P Glycolysis
ATP Glyceraldehyde
ADP ADP
ATP
NADH
NAD +
Glycerol
Disorders of galactose metabolism
Galactokinase Hereditary deficiency of galactokinase. Galactitol accumulates if galactose is present in diet.
deficiency Relatively mild condition. Autosomal recessive.
Symptoms: galactose appears in blood (galactosemia) and urine (galactosuria); infantile cataracts.
May present as failure to track objects or to develop a social smile. Galactokinase deficiency is
kinder (benign condition).
Classic galactosemia Absence of galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase. Autosomal recessive. Damage is caused by
accumulation of toxic substances (including galactitol, which accumulates in the lens of the eye).
Symptoms develop when infant begins feeding (lactose present in breast milk and routine formula)
and include failure to thrive, jaundice, hepatomegaly, infantile cataracts, intellectual disability. Can
predispose to E coli sepsis in neonates.
Treatment: exclude galactose and lactose (galactose + glucose) from diet.
Galactokinase Uridylyltransferase Fructose is to Aldolase B as Galactose is to
Galactose Galactose-1-P Glucose-1-P
UridylTransferase (FAB GUT).
ATP ADP The more serious defects lead to PO 4 depletion.
3−
Aldose UDP-Glu UDP-Gal
reductase
4-Epimerase Glycolysis/glycogenesis
Galactitol
FAS1_2019_01-Biochem.indd 80 11/7/19 3:16 PM