Page 127 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 127
BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—METABOlISM BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—METABOlISM SECTION II 83
Ornithine Most common urea cycle disorder. X-linked recessive (vs other urea cycle enzyme deficiencies,
transcarbamylase which are autosomal recessive). Interferes with the body’s ability to eliminate ammonia. Often
deficiency evident in the first few days of life, but may present later. Excess carbamoyl phosphate is converted
to orotic acid (part of the pyrimidine synthesis pathway).
Findings: orotic acid in blood and urine, BUN, symptoms of hyperammonemia. No
megaloblastic anemia (vs orotic aciduria).
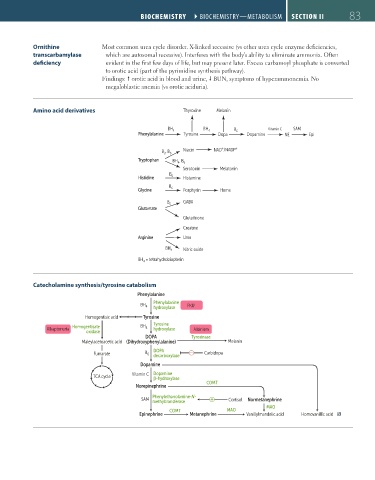
Amino acid derivatives Thyroxine Melanin
BH 4 BH 4 B 6 Vitamin C SAM
Phenylalanine Tyrosine Dopa Dopamine NE Epi
+
B , B 6 Niacin NAD /NADP +
2
Tryptophan BH , B 6
4
Serotonin Melatonin
B
Histidine 6 Histamine
B
Glycine 6 Porphyrin Heme
B 6 GABA
Glutamate
Glutathione
Creatine
Arginine Urea
BH 4 Nitric oxide
BH = tetrahydrobiopterin
4
Catecholamine synthesis/tyrosine catabolism
Phenylalanine
BH 4 Phenylalanine PKU
hydroxylase
Homogentisic acid Tyrosine
Homogentisate BH 4 Tyrosine
Alkaptonuria hydroxylase Albinism
oxidase
DOPA Tyrosinase
Maleylacetoacetic acid (Dihydroxyphenylalanine) Melanin
Fumarate B 6 DOPA – Carbidopa
decarboxylase
Dopamine
Vitamin C Dopamine
TCA cycle β-hydroxylase
COMT
Norepinephrine
Phenylethanolamine-N-
SAM Cortisol Normetanephrine
methyltransferase
MAO
COMT MAO
Epinephrine Metanephrine Vanillylmandelic acid Homovanillic acid
FAS1_2019_01-Biochem.indd 83 11/7/19 3:16 PM