Page 225 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 225
Microbiology ` microbiology—systems Microbiology ` microbiology—systems SEcTioN ii 181
Urinary tract Cystitis presents with dysuria, frequency, urgency, suprapubic pain, and WBCs (but not WBC
infections casts) in urine. Primarily caused by ascension of microbes from urethra to bladder. Ascension to
kidney results in pyelonephritis, which presents with fever, chills, flank pain, costovertebral angle
tenderness, hematuria, and WBC casts.
Ten times more common in women (shorter urethras colonized by fecal flora).
Risk factors: obstruction (eg, kidney stones, enlarged prostate), kidney surgery, catheterization,
congenital GU malformation (eg, vesicoureteral reflux), diabetes, pregnancy.
sPecies FeatUres commeNts
Escherichia coli Leading cause of UTI. Colonies show strong Diagnostic markers:
pink lactose-fermentation on MacConkey ⊕ Leukocyte esterase = evidence of WBC
agar. activity.
Staphylococcus 2nd leading cause of UTI in sexually active ⊕ Nitrite test = reduction of urinary nitrates
saprophyticus women. by gram ⊝ bacterial species (eg, E coli).
⊕ Urease test = urease-producing bugs (eg,
Klebsiella pneumoniae 3rd leading cause of UTI. Large mucoid capsule S saprophyticus, Proteus, Klebsiella).
and viscous colonies.
Serratia marcescens Some strains produce a red pigment; often
nosocomial and drug resistant.
Enterococcus Often nosocomial and drug resistant.
Proteus mirabilis Motility causes “swarming” on agar; associated
with struvite stones.
Pseudomonas Blue-green pigment and fruity odor; usually
aeruginosa nosocomial and drug resistant.
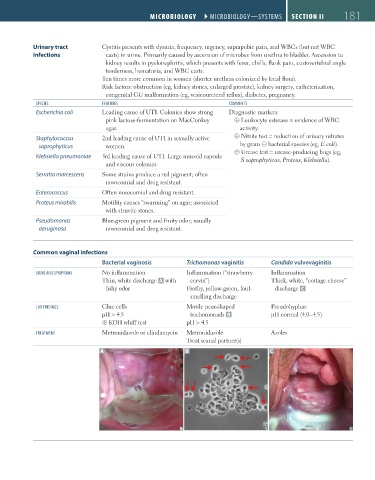
Common vaginal infections
Bacterial vaginosis Trichomonas vaginitis Candida vulvovaginitis
sigNs aND symPtoms No inflammation Inflammation (“strawberry Inflammation
Thin, white discharge A with cervix”) Thick, white, “cottage cheese”
fishy odor Frothy, yellow-green, foul- discharge C
smelling discharge
lab FiNDiNgs Clue cells Motile pear-shaped Pseudohyphae
pH > 4.5 trichomonads B pH normal (4.0–4.5)
⊕ KOH whiff test pH > 4.5
treatmeNt Metronidazole or clindamycin Metronidazole Azoles
Treat sexual partner(s)
A B C
FAS1_2019_03-Microbiology.indd 181 11/14/19 12:22 PM