Page 263 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 263
Pathology ` PATHOLOGY—InfLAMMATIOn Pathology ` PATHOLOGY—neOPLASIA SECtIoN II 219
` PATHOLOGY—neOPLASIA
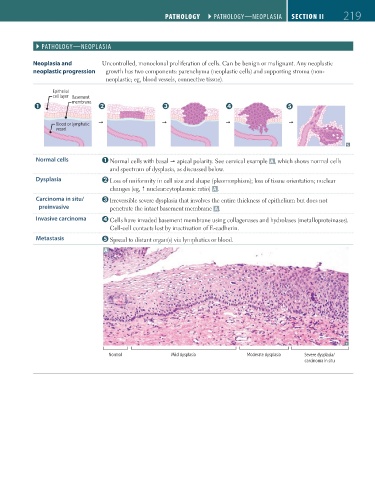
Neoplasia and Uncontrolled, monoclonal proliferation of cells. Can be benign or malignant. Any neoplastic
neoplastic progression growth has two components: parenchyma (neoplastic cells) and supporting stroma (non-
neoplastic; eg, blood vessels, connective tissue).
Epithelial
Epithelial
Epithelial
Epithelial
Epithelial
cell layer Basement
cell layer Basement
cell layer Basement
cell layer Basement
cell layer Basement
membrane
membrane
membrane
membrane
membrane
Blood or lymphatic
Blood or lymphatic
Blood or lymphatic
Blood or lymphatic
Blood or lymphatic
vessel
vessel
vessel
vessel
vessel
Normal cells Normal cells with basal apical polarity. See cervical example A , which shows normal cells
and spectrum of dysplasia, as discussed below.
Dysplasia Loss of uniformity in cell size and shape (pleomorphism); loss of tissue orientation; nuclear
changes (eg, nuclear:cytoplasmic ratio) A .
Carcinoma in situ/ Irreversible severe dysplasia that involves the entire thickness of epithelium but does not
preinvasive penetrate the intact basement membrane A .
Invasive carcinoma Cells have invaded basement membrane using collagenases and hydrolases (metalloproteinases).
Cell-cell contacts lost by inactivation of E-cadherin.
Metastasis Spread to distant organ(s) via lymphatics or blood.
A
Normal Mild dysplasia Moderate dysplasia Severe dysplasia/
carcinoma in situ
FAS1_2019_04-Pathol.indd 219 11/7/19 4:02 PM