Page 261 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 261
Pathology ` PATHOLOGY—InfLAMMATIOn Pathology ` PATHOLOGY—InfLAMMATIOn SECtIoN II 217
Granulomatous A pattern of chronic inflammation. Can be induced by persistent T-cell response to certain
inflammation infections (eg, TB), immune-mediated diseases, and foreign bodies. Granulomas “wall
off” a resistant stimulus without completely eradicating or degrading it persistent
inflammation fibrosis, organ damage.
HISTOLOGY Focus of epithelioid cells (activated macrophages with abundant pink cytoplasm) surrounded by
A lymphocytes and multinucleated giant cells (formed by fusion of several activated macrophages).
Two types:
Caseating: associated with Central necrosis. Seen with infectious etiologies (eg, TB, fungal).
Noncaseating A : no central necrosis. Seen with autoimmune diseases (eg, sarcoidosis, Crohn
disease).
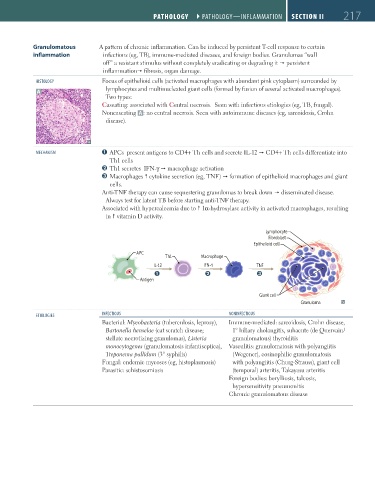
MeCHAnISM APCs present antigens to CD4+ Th cells and secrete IL-12 CD4+ Th cells differentiate into
Th1 cells
Th1 secretes IFN-γ macrophage activation
Macrophages cytokine secretion (eg, TNF) formation of epithelioid macrophages and giant
cells.
Anti-TNF therapy can cause sequestering granulomas to break down disseminated disease.
Always test for latent TB before starting anti-TNF therapy.
Associated with hypercalcemia due to 1α-hydroxylase activity in activated macrophages, resulting
in vitamin D activity.
Lymphocyte
Fibroblast
Epithelioid cell
APC
Th1 Macrophage
IL-12 IFN-γ TNF
Q R S
Antigen
Giant cell
Granuloma
eTIOLOGIeS InfeCTIOuS nOnInfeCTIOuS
Bacterial: Mycobacteria (tuberculosis, leprosy), Immune-mediated: sarcoidosis, Crohn disease,
Bartonella henselae (cat scratch disease; 1° biliary cholangitis, subacute (de Quervain/
stellate necrotizing granulomas), Listeria granulomatous) thyroiditis
monocytogenes (granulomatosis infantiseptica), Vasculitis: granulomatosis with polyangiitis
Treponema pallidum (3° syphilis) (Wegener), eosinophilic granulomatosis
Fungal: endemic mycoses (eg, histoplasmosis) with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss), giant cell
Parasitic: schistosomiasis (temporal) arteritis, Takayasu arteritis
Foreign bodies: berylliosis, talcosis,
hypersensitivity pneumonitis
Chronic granulomatous disease
FAS1_2019_04-Pathol.indd 217 11/7/19 4:02 PM