Page 264 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 264
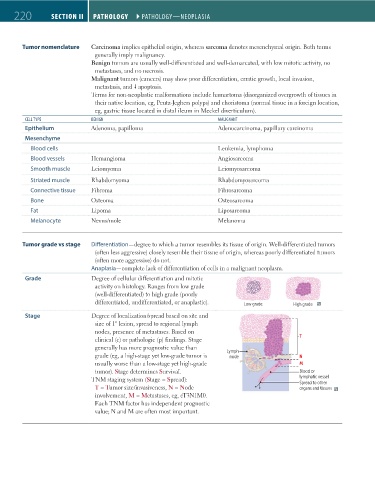
220 SECtIoN II Pathology ` PATHOLOGY—neOPLASIA Pathology ` PATHOLOGY—neOPLASIA
Tumor nomenclature Carcinoma implies epithelial origin, whereas sarcoma denotes mesenchymal origin. Both terms
generally imply malignancy.
Benign tumors are usually well-differentiated and well-demarcated, with low mitotic activity, no
metastases, and no necrosis.
Malignant tumors (cancers) may show poor differentiation, erratic growth, local invasion,
metastasis, and apoptosis.
Terms for non-neoplastic malformations include hamartoma (disorganized overgrowth of tissues in
their native location, eg, Peutz-Jeghers polyps) and choristoma (normal tissue in a foreign location,
eg, gastric tissue located in distal ileum in Meckel diverticulum).
CeLL TYPe BenIGn MALIGnAnT
Epithelium Adenoma, papilloma Adenocarcinoma, papillary carcinoma
Mesenchyme
Blood cells Leukemia, lymphoma
Blood vessels Hemangioma Angiosarcoma
Smooth muscle Leiomyoma Leiomyosarcoma
Striated muscle Rhabdomyoma Rhabdomyosarcoma
Connective tissue Fibroma Fibrosarcoma
Bone Osteoma Osteosarcoma
Fat Lipoma Liposarcoma
Melanocyte Nevus/mole Melanoma
Tumor grade vs stage Differentiation—degree to which a tumor resembles its tissue of origin. Well-differentiated tumors
(often less aggressive) closely resemble their tissue of origin, whereas poorly differentiated tumors
(often more aggressive) do not.
Anaplasia—complete lack of differentiation of cells in a malignant neoplasm.
Grade Degree of cellular differentiation and mitotic
activity on histology. Ranges from low grade
(well-differentiated) to high grade (poorly Low grade High grade
differentiated, undifferentiated, or anaplastic). Low grade High grade
Stage Degree of localization/spread based on site and
size of 1° lesion, spread to regional lymph
nodes, presence of metastases. Based on
clinical (c) or pathologic (p) findings. Stage T
generally has more prognostic value than T
grade (eg, a high-stage yet low-grade tumor is Lymph N
node
Lymph
usually worse than a low-stage yet high-grade node N M
tumor). Stage determines Survival. M Blood or
TNM staging system (Stage = Spread): lymphatic vessel
Blood or
Spread to other
lymphatic vessel
T = Tumor size/invasiveness, N = Node organs and tissues
Spread to other
involvement, M = Metastases, eg, cT3N1M0. organs and tissues
Each TNM factor has independent prognostic
value; N and M are often most important.
FAS1_2019_04-Pathol.indd 220 11/7/19 4:02 PM