Page 291 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 291
Pharmacology ` PHARMACOLOGY—AUTONOMIC dRUGS Pharmacology ` PHARMACOLOGY—AUTONOMIC dRUGS SEcTIoN II 247
+
+
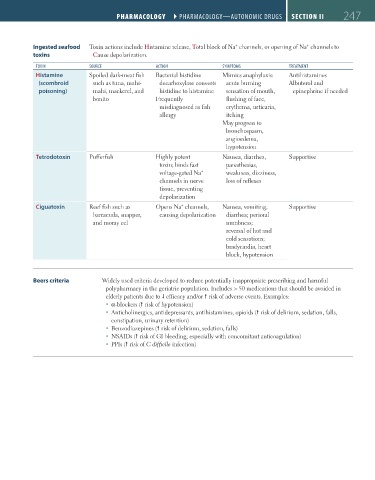
Ingested seafood Toxin actions include Histamine release, Total block of Na channels, or opening of Na channels to
toxins Cause depolarization.
TOXIN SOURCE ACTION SYMPTOMS TREATMENT
Histamine Spoiled dark-meat fish Bacterial histidine Mimics anaphylaxis: Antihistamines
(scombroid such as tuna, mahi- decarboxylase converts acute burning Albuterol and
poisoning) mahi, mackerel, and histidine to histamine sensation of mouth, epinephrine if needed
bonito Frequently flushing of face,
misdiagnosed as fish erythema, urticaria,
allergy itching
May progress to
bronchospasm,
angioedema,
hypotension
Tetrodotoxin Pufferfish Highly potent Nausea, diarrhea, Supportive
toxin; binds fast paresthesias,
+
voltage-gated Na weakness, dizziness,
channels in nerve loss of reflexes
tissue, preventing
depolarization
+
Ciguatoxin Reef fish such as Opens Na channels, Nausea, vomiting, Supportive
barracuda, snapper, causing depolarization diarrhea; perioral
and moray eel numbness;
reversal of hot and
cold sensations;
bradycardia, heart
block, hypotension
Beers criteria Widely used criteria developed to reduce potentially inappropriate prescribing and harmful
polypharmacy in the geriatric population. Includes > 50 medications that should be avoided in
elderly patients due to efficacy and/or risk of adverse events. Examples:
α-blockers ( risk of hypotension)
Anticholinergics, antidepressants, antihistamines, opioids ( risk of delirium, sedation, falls,
constipation, urinary retention)
Benzodiazepines ( risk of delirium, sedation, falls)
NSAIDs ( risk of GI bleeding, especially with concomitant anticoagulation)
PPIs ( risk of C difficile infection)
FAS1_2019_05-Pharmacology.indd 247 11/7/19 4:08 PM