Page 378 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 378
334 SEcTion iii EndocrinE ` endocrine—Physiology EndocrinE ` endocrine—Physiology
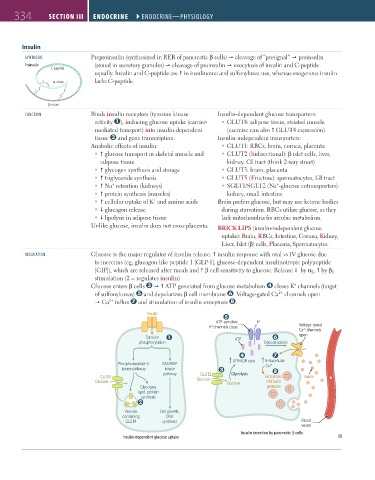
Insulin
synthesis Preproinsulin (synthesized in RER of pancreatic β cells) cleavage of “presignal” proinsulin
Proinsulin (stored in secretory granules) cleavage of proinsulin exocytosis of insulin and C-peptide
C-peptide
equally. Insulin and C-peptide are in insulinoma and sulfonylurea use, whereas exogenous insulin
S α-chain lacks C-peptide.
S
S
S S
S
β-chain
FUnction Binds insulin receptors (tyrosine kinase Insulin-dependent glucose transporters:
activity ), inducing glucose uptake (carrier- GLUT4: adipose tissue, striated muscle
mediated transport) into insulin-dependent (exercise can also GLUT4 expression)
tissue and gene transcription. Insulin-independent transporters:
Anabolic effects of insulin: GLUT1: RBCs, brain, cornea, placenta
glucose transport in skeletal muscle and GLUT2 (bidirectional): β islet cells, liver,
adipose tissue kidney, GI tract (think 2-way street)
glycogen synthesis and storage GLUT3: brain, placenta
triglyceride synthesis GLUT5 (Fructose): spermatocytes, GI tract
Na retention (kidneys) SGLT1/SGLT2 (Na -glucose cotransporters):
+
+
protein synthesis (muscles) kidney, small intestine
cellular uptake of K and amino acids Brain prefers glucose, but may use ketone bodies
+
glucagon release during starvation. RBCs utilize glucose, as they
lipolysis in adipose tissue lack mitochondria for aerobic metabolism.
Unlike glucose, insulin does not cross placenta. BRICK LIPS (insulin-independent glucose
uptake): Brain, RBCs, Intestine, Cornea, Kidney,
Liver, Islet (β) cells, Placenta, Spermatocytes.
regUlAtion Glucose is the major regulator of insulin release. insulin response with oral vs IV glucose due
to incretins (eg, glucagon-like peptide 1 [GLP-1], glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide
[GIP]), which are released after meals and β cell sensitivity to glucose. Release by α 2 , by β 2
stimulation (2 = regulates insulin)
+
Glucose enters β cells ATP generated from glucose metabolism closes K channels (target
of sulfonylureas) and depolarizes β cell membrane . Voltage-gated Ca channels open
2+
2+
Ca influx and stimulation of insulin exocytosis .
Insulin
Insulin
ATP-sensitive K +
K channels close Voltage-gated
+
Ca channels
2+
open
Tyrosine ATP
phosphorylation Depolarization
ATP/ADP ratio Intracellular
Phosphoinositide-3 RAS/MAP Ca 2+
kinase pathway kinase
pathway GLUT2 Glycolysis
GLUT4 Exocytosis Insulin
Glucose Glucose Glucose of insulin
Glycogen, granules
lipid, protein
synthesis
Vesicles Cell growth,
containing DNA
GLUT4 synthesis Blood
vessel
Insulin secretion by pancreatic β cells
Insulin-dependent glucose uptake
FAS1_2019_08-Endocrine.indd 334 11/7/19 4:30 PM