Page 381 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 381
EndocrinE ` endocrine—Physiology EndocrinE ` endocrine—Physiology SEcTion iii 337
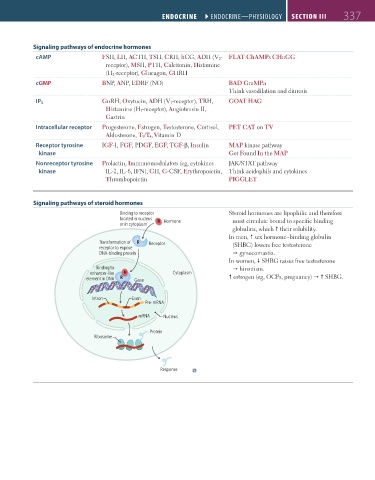
Signaling pathways of endocrine hormones
cAMP FSH, LH, ACTH, TSH, CRH, hCG, ADH (V 2 - FLAT ChAMPs CHuGG
receptor), MSH, PTH, Calcitonin, Histamine
(H 2 -receptor), Glucagon, GHRH
cGMP BNP, ANP, EDRF (NO) BAD GraMPa
Think vasodilation and diuresis
IP 3 GnRH, Oxytocin, ADH (V 1 -receptor), TRH, GOAT HAG
Histamine (H 1 -receptor), Angiotensin II,
Gastrin
Intracellular receptor Progesterone, Estrogen, Testosterone, Cortisol, PET CAT on TV
Aldosterone, T 3 /T 4 , Vitamin D
Receptor tyrosine IGF-1, FGF, PDGF, EGF, TGF-β, Insulin MAP kinase pathway
kinase Get Found In the MAP
Nonreceptor tyrosine Prolactin, Immunomodulators (eg, cytokines JAK/STAT pathway
kinase IL-2, IL-6, IFN), GH, G-CSF, Erythropoietin, Think acidophils and cytokines
Thrombopoietin PIGGLET
Signaling pathways of steroid hormones
Binding to receptor Steroid hormones are lipophilic and therefore
located in nucleus H Hormone must circulate bound to specific binding
or in cytoplasm
globulins, which their solubility.
In men, sex hormone–binding globulin
Transformation of R Receptor (SHBG) lowers free testosterone
receptor to expose
DNA-binding protein gynecomastia.
In women, SHBG raises free testosterone
Binding to hirsutism.
enhancer-like H Cytoplasm
element in DNA R Gene estrogen (eg, OCPs, pregnancy) SHBG.
Intron Exon
Pre-mRNA
mRNA Nucleus
Protein
Ribosome
Response
FAS1_2019_08-Endocrine.indd 337 11/7/19 4:30 PM