Page 380 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 380
336 SEcTion iii EndocrinE ` endocrine—Physiology EndocrinE ` endocrine—Physiology
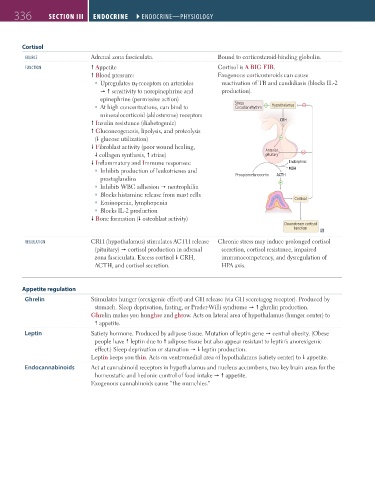
Cortisol
soUrce Adrenal zona fasciculata. Bound to corticosteroid-binding globulin.
FUnction Appetite Cortisol is A BIG FIB.
Blood pressure: Exogenous corticosteroids can cause
Upregulates α 1 -receptors on arterioles reactivation of TB and candidiasis (blocks IL-2
sensitivity to norepinephrine and production).
epinephrine (permissive action)
At high concentrations, can bind to Stress Hypothalamus
Circadian rhythm
mineralocorticoid (aldosterone) receptors
Insulin resistance (diabetogenic) CRH
Gluconeogenesis, lipolysis, and proteolysis
( glucose utilization)
Fibroblast activity (poor wound healing, Anterior
collagen synthesis, striae) pituitary
Inflammatory and Immune responses: Endorphins
Inhibits production of leukotrienes and MSH
prostaglandins Proopiomelanocortin ACTH
Inhibits WBC adhesion neutrophilia
Blocks histamine release from mast cells
Eosinopenia, lymphopenia Cortisol
Blocks IL-2 production
Bone formation ( osteoblast activity)
Downstream cortisol
function
regUlAtion CRH (hypothalamus) stimulates ACTH release Chronic stress may induce prolonged cortisol
(pituitary) cortisol production in adrenal secretion, cortisol resistance, impaired
zona fasciculata. Excess cortisol CRH, immunocompetency, and dysregulation of
ACTH, and cortisol secretion. HPA axis.
Appetite regulation
Ghrelin Stimulates hunger (orexigenic effect) and GH release (via GH secretagog receptor). Produced by
stomach. Sleep deprivation, fasting, or Prader-Willi syndrome ghrelin production.
Ghrelin makes you hunghre and ghrow. Acts on lateral area of hypothalamus (hunger center) to
appetite.
Leptin Satiety hormone. Produced by adipose tissue. Mutation of leptin gene central obesity. (Obese
people have leptin due to adipose tissue but also appear resistant to leptin’s anorexigenic
effect.) Sleep deprivation or starvation leptin production.
Leptin keeps you thin. Acts on ventromedial area of hypothalamus (satiety center) to appetite.
Endocannabinoids Act at cannabinoid receptors in hypothalamus and nucleus accumbens, two key brain areas for the
homeostatic and hedonic control of food intake appetite.
Exogenous cannabinoids cause “the munchies.”
FAS1_2019_08-Endocrine.indd 336 11/7/19 4:30 PM