Page 414 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 414
370 seCtion iii Gastrointestinal ` gastrointestinal—anatomy Gastrointestinal ` gastrointestinal—PHysiology
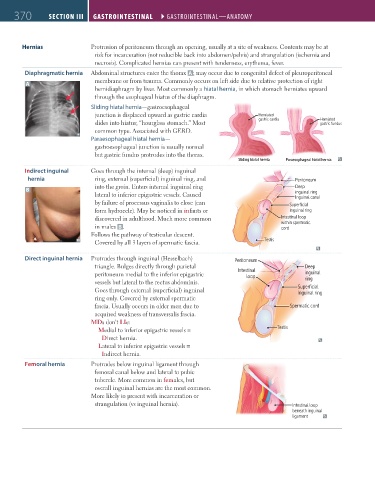
Hernias Protrusion of peritoneum through an opening, usually at a site of weakness. Contents may be at
risk for incarceration (not reducible back into abdomen/pelvis) and strangulation (ischemia and
necrosis). Complicated hernias can present with tenderness, erythema, fever.
Diaphragmatic hernia Abdominal structures enter the thorax A ; may occur due to congenital defect of pleuroperitoneal
membrane or from trauma. Commonly occurs on left side due to relative protection of right
A
hemidiaphragm by liver. Most commonly a hiatal hernia, in which stomach herniates upward
through the esophageal hiatus of the diaphragm.
Sliding hiatal hernia—gastroesophageal
junction is displaced upward as gastric cardia Herniated
slides into hiatus; “hourglass stomach.” Most gastric cardia Herniated
gastric fundus
common type. Associated with GERD.
Paraesophageal hiatal hernia—
gastroesophageal junction is usually normal
but gastric fundus protrudes into the thorax.
Sliding hiatal hernia Paraesophageal hiatal hernia
Indirect inguinal Goes through the internal (deep) inguinal
hernia ring, external (superficial) inguinal ring, and Peritoneum
B into the groin. Enters internal inguinal ring Deep
lateral to inferior epigastric vessels. Caused inguinal ring
Inguinal canal
by failure of processus vaginalis to close (can Superficial
form hydrocele). May be noticed in infants or inguinal ring
discovered in adulthood. Much more common Intestinal loop
in males B . within spermatic
cord
Follows the pathway of testicular descent.
Covered by all 3 layers of spermatic fascia. Testis
Direct inguinal hernia Protrudes through inguinal (Hesselbach) Peritoneum
triangle. Bulges directly through parietal Deep
peritoneum medial to the inferior epigastric Intestinal inguinal
loop
vessels but lateral to the rectus abdominis. ring
Goes through external (superficial) inguinal Superficial
inguinal ring
ring only. Covered by external spermatic
fascia. Usually occurs in older men due to Spermatic cord
acquired weakness of transversalis fascia.
MDs don’t LIe:
Medial to inferior epigastric vessels = Testis
Direct hernia.
Lateral to inferior epigastric vessels =
Indirect hernia.
Femoral hernia Protrudes below inguinal ligament through
femoral canal below and lateral to pubic
tubercle. More common in females, but
overall inguinal hernias are the most common.
More likely to present with incarceration or
strangulation (vs inguinal hernia). Intestinal loop
beneath inguinal
ligament
FAS1_2019_09-Gastrointestinal.indd 370 11/7/19 4:42 PM