Page 427 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 427
Gastrointestinal ` gastrointestinal—PatHology Gastrointestinal ` gastrointestinal—PatHology seCtion iii 383
Irritable bowel Recurrent abdominal pain associated with ≥ 2 of the following:
syndrome Related to defecation
Change in stool frequency
Change in form (consistency) of stool
No structural abnormalities. Most common in middle-aged women. Chronic symptoms may be
diarrhea-predominant, constipation-predominant, or mixed. Pathophysiology is multifaceted.
First-line treatment is lifestyle modification and dietary changes.
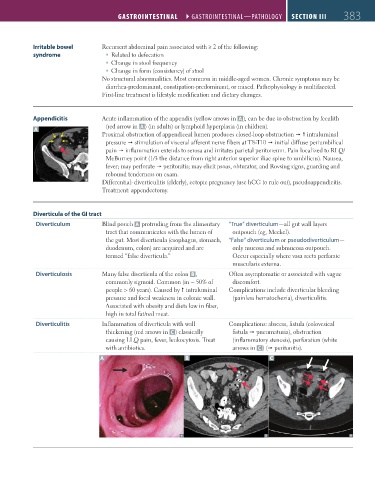
Appendicitis Acute inflammation of the appendix (yellow arrows in A ), can be due to obstruction by fecalith
(red arrow in A ) (in adults) or lymphoid hyperplasia (in children).
A
Proximal obstruction of appendiceal lumen produces closed-loop obstruction intraluminal
pressure stimulation of visceral afferent nerve fibers at T8-T10 initial diffuse periumbilical
pain inflammation extends to serosa and irritates parietal peritoneum. Pain localized to RLQ/
McBurney point (1/3 the distance from right anterior superior iliac spine to umbilicus). Nausea,
fever; may perforate peritonitis; may elicit psoas, obturator, and Rovsing signs, guarding and
rebound tenderness on exam.
Differential: diverticulitis (elderly), ectopic pregnancy (use hCG to rule out), pseudoappendicitis.
Treatment: appendectomy.
Diverticula of the GI tract
Diverticulum Blind pouch A protruding from the alimentary “True” diverticulum—all gut wall layers
tract that communicates with the lumen of outpouch (eg, Meckel).
the gut. Most diverticula (esophagus, stomach, “False” diverticulum or pseudodiverticulum—
duodenum, colon) are acquired and are only mucosa and submucosa outpouch.
termed “false diverticula.” Occur especially where vasa recta perforate
muscularis externa.
Diverticulosis Many false diverticula of the colon B , Often asymptomatic or associated with vague
commonly sigmoid. Common (in ~ 50% of discomfort.
people > 60 years). Caused by intraluminal Complications include diverticular bleeding
pressure and focal weakness in colonic wall. (painless hematochezia), diverticulitis.
Associated with obesity and diets low in fiber,
high in total fat/red meat.
Diverticulitis Inflammation of diverticula with wall Complications: abscess, fistula (colovesical
thickening (red arrows in C ) classically fistula pneumaturia), obstruction
causing LLQ pain, fever, leukocytosis. Treat (inflammatory stenosis), perforation (white
with antibiotics. arrows in C ) ( peritonitis).
A B C
FAS1_2019_09-Gastrointestinal.indd 383 11/7/19 4:42 PM