Page 428 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 428
384 seCtion iii Gastrointestinal ` gastrointestinal—PatHology Gastrointestinal ` gastrointestinal—PatHology
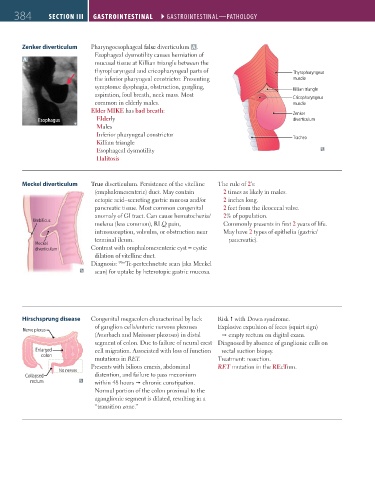
Zenker diverticulum Pharyngoesophageal false diverticulum A .
Esophageal dysmotility causes herniation of
A
mucosal tissue at Killian triangle between the
thyropharyngeal and cricopharyngeal parts of Thyropharyngeus
the inferior pharyngeal constrictor. Presenting muscle
symptoms: dysphagia, obstruction, gurgling, Killian triangle
aspiration, foul breath, neck mass. Most Cricopharyngeus
common in elderly males. muscle
Elder MIKE has bad breath: Zenker
Esophagus Elderly diverticulum
Males
Inferior pharyngeal constrictor
Killian triangle Trachea
Esophageal dysmotility
Halitosis
Meckel diverticulum True diverticulum. Persistence of the vitelline The rule of 2’s:
(omphalomesenteric) duct. May contain 2 times as likely in males.
ectopic acid–secreting gastric mucosa and/or 2 inches long.
pancreatic tissue. Most common congenital 2 feet from the ileocecal valve.
anomaly of GI tract. Can cause hematochezia/ 2% of population.
Umbilicus
melena (less common), RLQ pain, Commonly presents in first 2 years of life.
intussusception, volvulus, or obstruction near May have 2 types of epithelia (gastric/
terminal ileum. pancreatic).
Meckel
diverticulum Contrast with omphalomesenteric cyst = cystic
dilation of vitelline duct.
Diagnosis: 99m Tc-pertechnetate scan (aka Meckel
scan) for uptake by heterotopic gastric mucosa.
Hirschsprung disease Congenital megacolon characterized by lack Risk with Down syndrome.
of ganglion cells/enteric nervous plexuses Explosive expulsion of feces (squirt sign)
Nerve plexus
(Auerbach and Meissner plexuses) in distal empty rectum on digital exam.
segment of colon. Due to failure of neural crest Diagnosed by absence of ganglionic cells on
Enlarged cell migration. Associated with loss of function rectal suction biopsy.
colon
mutations in RET. Treatment: resection.
Presents with bilious emesis, abdominal RET mutation in the REcTum.
No nerves
Collapsed distention, and failure to pass meconium
rectum within 48 hours chronic constipation.
Normal portion of the colon proximal to the
aganglionic segment is dilated, resulting in a
“transition zone.”
FAS1_2019_09-Gastrointestinal.indd 384 11/7/19 4:42 PM