Page 430 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 430
386 seCtion iii Gastrointestinal ` gastrointestinal—PatHology Gastrointestinal ` gastrointestinal—PatHology
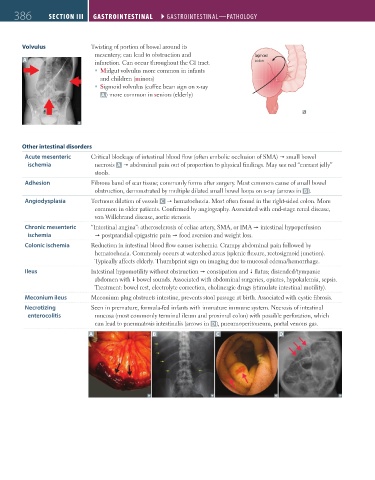
Volvulus Twisting of portion of bowel around its
mesentery; can lead to obstruction and Sigmoid
A colon
infarction. Can occur throughout the GI tract.
Midgut volvulus more common in infants
and children (minors)
Sigmoid volvulus (coffee bean sign on x-ray
A ) more common in seniors (elderly)
Other intestinal disorders
Acute mesenteric Critical blockage of intestinal blood flow (often embolic occlusion of SMA) small bowel
ischemia necrosis A abdominal pain out of proportion to physical findings. May see red “currant jelly”
stools.
Adhesion Fibrous band of scar tissue; commonly forms after surgery. Most common cause of small bowel
obstruction, demonstrated by multiple dilated small bowel loops on x-ray (arrows in B ).
Angiodysplasia Tortuous dilation of vessels C hematochezia. Most often found in the right-sided colon. More
common in older patients. Confirmed by angiography. Associated with end-stage renal disease,
von Willebrand disease, aortic stenosis.
Chronic mesenteric “Intestinal angina”: atherosclerosis of celiac artery, SMA, or IMA intestinal hypoperfusion
ischemia postprandial epigastric pain food aversion and weight loss.
Colonic ischemia Reduction in intestinal blood flow causes ischemia. Crampy abdominal pain followed by
hematochezia. Commonly occurs at watershed areas (splenic flexure, rectosigmoid junction).
Typically affects elderly. Thumbprint sign on imaging due to mucosal edema/hemorrhage.
Ileus Intestinal hypomotility without obstruction constipation and flatus; distended/tympanic
abdomen with bowel sounds. Associated with abdominal surgeries, opiates, hypokalemia, sepsis.
Treatment: bowel rest, electrolyte correction, cholinergic drugs (stimulate intestinal motility).
Meconium ileus Meconium plug obstructs intestine, prevents stool passage at birth. Associated with cystic fibrosis.
Necrotizing Seen in premature, formula-fed infants with immature immune system. Necrosis of intestinal
enterocolitis mucosa (most commonly terminal ileum and proximal colon) with possible perforation, which
can lead to pneumatosis intestinalis (arrows in D), pneumoperitoneum, portal venous gas.
A B C D
FAS1_2019_09-Gastrointestinal.indd 386 11/7/19 4:42 PM