Page 442 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 442
398 seCtion iii Gastrointestinal ` gastrointestinal—PHarmaCology Gastrointestinal ` gastrointestinal—PHarmaCology
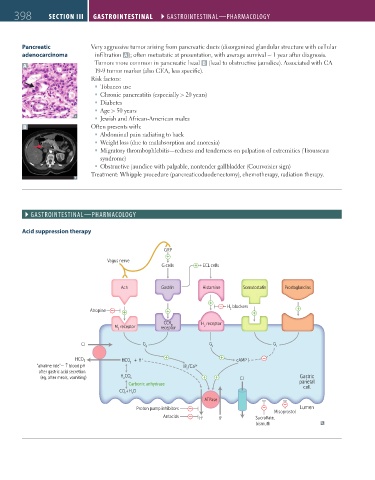
Pancreatic Very aggressive tumor arising from pancreatic ducts (disorganized glandular structure with cellular
adenocarcinoma infiltration A ); often metastatic at presentation, with average survival ~ 1 year after diagnosis.
Tumors more common in pancreatic head B (lead to obstructive jaundice). Associated with CA
A
19-9 tumor marker (also CEA, less specific).
Risk factors:
Tobacco use
Chronic pancreatitis (especially > 20 years)
Diabetes
Age > 50 years
Jewish and African-American males
B Often presents with:
Abdominal pain radiating to back
Weight loss (due to malabsorption and anorexia)
Migratory thrombophlebitis—redness and tenderness on palpation of extremities (Trousseau
syndrome)
Obstructive jaundice with palpable, nontender gallbladder (Courvoisier sign)
Treatment: Whipple procedure (pancreaticoduodenectomy), chemotherapy, radiation therapy.
` gastrointestinal—PHarmaCology
Acid suppression therapy
GRP
Vagus nerve
G cells ECL cells
Ach Gastrin Histamine Somatostatin Prostaglandins
H blockers
2
Atropine
CCK H receptor
B
M receptor receptor 2
3
CI – G q G s G i
– –
HCO 3 HCO +H + cAMP
3
”alkaline tide”— ↑ blood pH IP /Ca 2+
3
after gastric acid secretion
(eg, after meals, vomiting) H CO 3 CI – Gastric
2
Carbonic anhydrase parietal
cell
CO + H O
2 2
ATPase
Proton pump inhibitors Lumen
Misoprostol
Antacids H + K + Sucralfate,
bismuth
FAS1_2019_09-Gastrointestinal.indd 398 11/7/19 4:42 PM