Page 438 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 438
394 seCtion iii Gastrointestinal ` gastrointestinal—PatHology Gastrointestinal ` gastrointestinal—PatHology
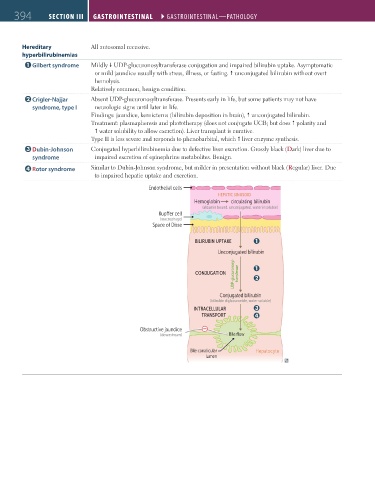
Hereditary All autosomal recessive.
hyperbilirubinemias
Gilbert syndrome Mildly UDP-glucuronosyltransferase conjugation and impaired bilirubin uptake. Asymptomatic
or mild jaundice usually with stress, illness, or fasting. unconjugated bilirubin without overt
hemolysis.
Relatively common, benign condition.
Crigler-Najjar Absent UDP-glucuronosyltransferase. Presents early in life, but some patients may not have
syndrome, type I neurologic signs until later in life.
Findings: jaundice, kernicterus (bilirubin deposition in brain), unconjugated bilirubin.
Treatment: plasmapheresis and phototherapy (does not conjugate UCB; but does polarity and
water solubility to allow excretion). Liver transplant is curative.
Type II is less severe and responds to phenobarbital, which liver enzyme synthesis.
Dubin-Johnson Conjugated hyperbilirubinemia due to defective liver excretion. Grossly black (Dark) liver due to
syndrome impaired excretion of epinephrine metabolites. Benign.
Rotor syndrome Similar to Dubin-Johnson syndrome, but milder in presentation without black (Regular) liver. Due
to impaired hepatic uptake and excretion.
Endothelial cells
HEPATIC SINUSOID
Hemoglobin circulating bilirubin
(albumin bound, unconjugated, water insoluble)
Kup
er cell
(macrophage)
Space of Disse
BILIRUBIN UPTAKE Q
Unconjugated bilirubin
UDP-glucuronosyl- transferase R
CONJUGATION Q
Conjugated bilirubin
(bilirubin diglucuronide, water soluble)
INTRACELLULAR S
TRANSPORT T
Obstructive jaundice
(downstream) Bile flow
Bile canalicular Hepatocyte
lumen
FAS1_2019_09-Gastrointestinal.indd 394 11/7/19 4:42 PM