Page 439 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 439
Gastrointestinal ` gastrointestinal—PatHology Gastrointestinal ` gastrointestinal—PatHology seCtion iii 395
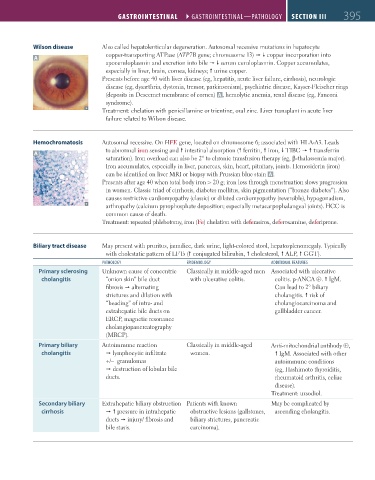
Wilson disease Also called hepatolenticular degeneration. Autosomal recessive mutations in hepatocyte
copper-transporting ATPase (ATP7B gene; chromosome 13) copper incorporation into
A
apoceruloplasmin and excretion into bile serum ceruloplasmin. Copper accumulates,
especially in liver, brain, cornea, kidneys; urine copper.
Presents before age 40 with liver disease (eg, hepatitis, acute liver failure, cirrhosis), neurologic
disease (eg, dysarthria, dystonia, tremor, parkinsonism), psychiatric disease, Kayser-Fleischer rings
(deposits in Descemet membrane of cornea) A , hemolytic anemia, renal disease (eg, Fanconi
syndrome).
Treatment: chelation with penicillamine or trientine, oral zinc. Liver transplant in acute liver
failure related to Wilson disease.
Hemochromatosis Autosomal recessive. On HFE gene, located on chromosome 6; associated with HLA-A3. Leads
to abnormal iron sensing and intestinal absorption ( ferritin, iron, TIBC transferrin
A
saturation). Iron overload can also be 2° to chronic transfusion therapy (eg, β-thalassemia major).
Iron accumulates, especially in liver, pancreas, skin, heart, pituitary, joints. Hemosiderin (iron)
can be identified on liver MRI or biopsy with Prussian blue stain A .
Presents after age 40 when total body iron > 20 g; iron loss through menstruation slows progression
in women. Classic triad of cirrhosis, diabetes mellitus, skin pigmentation (“bronze diabetes”). Also
causes restrictive cardiomyopathy (classic) or dilated cardiomyopathy (reversible), hypogonadism,
arthropathy (calcium pyrophosphate deposition; especially metacarpophalangeal joints). HCC is
common cause of death.
Treatment: repeated phlebotomy, iron (Fe) chelation with deferasirox, deferoxamine, deferiprone.
Biliary tract disease May present with pruritus, jaundice, dark urine, light-colored stool, hepatosplenomegaly. Typically
with cholestatic pattern of LFTs ( conjugated bilirubin, cholesterol, ALP, GGT).
PatHology ePiDemiology aDDitional FeatUres
Primary sclerosing Unknown cause of concentric Classically in middle-aged men Associated with ulcerative
cholangitis “onion skin” bile duct with ulcerative colitis. colitis. p-ANCA ⊕. IgM.
fibrosis alternating Can lead to 2° biliary
strictures and dilation with cholangitis. risk of
“beading” of intra- and cholangiocarcinoma and
extrahepatic bile ducts on gallbladder cancer.
ERCP, magnetic resonance
cholangiopancreatography
(MRCP).
Primary biliary Autoimmune reaction Classically in middle-aged Anti-mitochondrial antibody ⊕,
cholangitis lymphocytic infiltrate women. IgM. Associated with other
+/– granulomas autoimmune conditions
destruction of lobular bile (eg, Hashimoto thyroiditis,
ducts. rheumatoid arthritis, celiac
disease).
Treatment: ursodiol.
Secondary biliary Extrahepatic biliary obstruction Patients with known May be complicated by
cirrhosis pressure in intrahepatic obstructive lesions (gallstones, ascending cholangitis.
ducts injury/ fibrosis and biliary strictures, pancreatic
bile stasis. carcinoma).
FAS1_2019_09-Gastrointestinal.indd 395 11/7/19 4:42 PM