Page 514 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 514
470 section iii Musculoskeletal, skin, and connective tissue ` pathology Musculoskeletal, skin, and connective tissue ` pathology
Systemic lupus Systemic, remitting, and relapsing autoimmune disease. Organ damage primarily due to a type III
erythematosus hypersensitivity reaction and, to a lesser degree, a type II hypersensitivity reaction. Associated with
deficiency of early complement proteins (eg, C1q, C4, C2) clearance of immune complexes.
Classic presentation: rash, joint pain, and fever in a female of reproductive age (especially of
African-American or Hispanic descent).
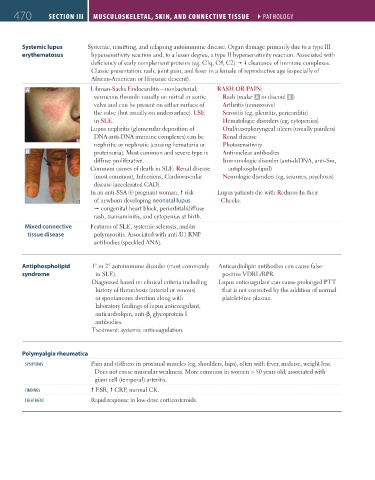
A Libman-Sacks Endocarditis—nonbacterial, RASH OR PAIN:
verrucous thrombi usually on mitral or aortic Rash (malar A or discoid B )
valve and can be present on either surface of Arthritis (nonerosive)
the valve (but usually on undersurface). LSE Serositis (eg, pleuritis, pericarditis)
in SLE. Hematologic disorders (eg, cytopenias)
Lupus nephritis (glomerular deposition of Oral/nasopharyngeal ulcers (usually painless)
DNA-anti-DNA immune complexes) can be Renal disease
nephritic or nephrotic (causing hematuria or Photosensitivity
B proteinuria). Most common and severe type is Antinuclear antibodies
diffuse proliferative. Immunologic disorder (anti-dsDNA, anti-Sm,
Common causes of death in SLE: Renal disease antiphospholipid)
(most common), Infections, Cardiovascular Neurologic disorders (eg, seizures, psychosis)
disease (accelerated CAD).
In an anti-SSA ⊕ pregnant woman, risk Lupus patients die with Redness In their
of newborn developing neonatal lupus Cheeks.
congenital heart block, periorbital/diffuse
rash, transaminitis, and cytopenias at birth.
Mixed connective Features of SLE, systemic sclerosis, and/or
tissue disease polymyositis. Associated with anti-U1 RNP
antibodies (speckled ANA).
Antiphospholipid 1° or 2° autoimmune disorder (most commonly Anticardiolipin antibodies can cause false-
syndrome in SLE). positive VDRL/RPR.
Diagnosed based on clinical criteria including Lupus anticoagulant can cause prolonged PTT
history of thrombosis (arterial or venous) that is not corrected by the addition of normal
or spontaneous abortion along with platelet-free plasma.
laboratory findings of lupus anticoagulant,
anticardiolipin, anti-β glycoprotein I
2
antibodies.
Treatment: systemic anticoagulation.
Polymyalgia rheumatica
symptoms Pain and stiffness in proximal muscles (eg, shoulders, hips), often with fever, malaise, weight loss.
Does not cause muscular weakness. More common in women > 50 years old; associated with
giant cell (temporal) arteritis.
Findings ESR, CRP, normal CK.
tREatmEnt Rapid response to low-dose corticosteroids.
FAS1_2019_11-Musculo.indd 470 11/7/19 5:23 PM