Page 512 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 512
468 section iii Musculoskeletal, skin, and connective tissue ` pathology Musculoskeletal, skin, and connective tissue ` pathology
Systemic juvenile Systemic arthritis seen in < 16 year olds. Usually presents with daily spiking fevers, salmon-
idiopathic arthritis pink macular rash, arthritis (commonly 2+ joints). Associated with anterior uveitis. Frequently
presents with leukocytosis, thrombocytosis, anemia, ESR, CRP. Treatment: NSAIDs, steroids,
methotrexate, TNF inhibitors.
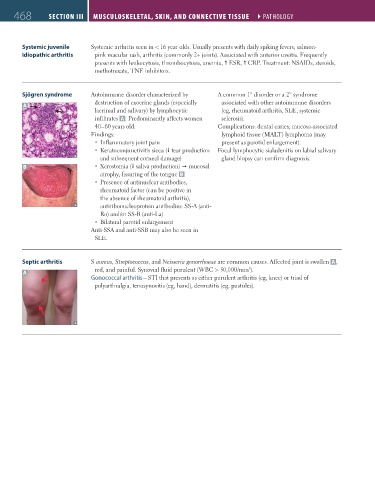
Sjögren syndrome Autoimmune disorder characterized by A common 1° disorder or a 2° syndrome
destruction of exocrine glands (especially associated with other autoimmune disorders
A
lacrimal and salivary) by lymphocytic (eg, rheumatoid arthritis, SLE, systemic
infiltrates A . Predominantly affects women sclerosis).
40–60 years old. Complications: dental caries; mucosa-associated
Findings: lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma (may
Inflammatory joint pain present as parotid enlargement).
Keratoconjunctivitis sicca ( tear production Focal lymphocytic sialadenitis on labial salivary
and subsequent corneal damage) gland biopsy can confirm diagnosis.
B Xerostomia ( saliva production) mucosal
atrophy, fissuring of the tongue B
Presence of antinuclear antibodies,
rheumatoid factor (can be positive in
the absence of rheumatoid arthritis),
antiribonucleoprotein antibodies: SS-A (anti-
Ro) and/or SS-B (anti-La)
Bilateral parotid enlargement
Anti-SSA and anti-SSB may also be seen in
SLE.
Septic arthritis S aureus, Streptococcus, and Neisseria gonorrhoeae are common causes. Affected joint is swollen A ,
red, and painful. Synovial fluid purulent (WBC > 50,000/mm ).
3
A
Gonococcal arthritis—STI that presents as either purulent arthritis (eg, knee) or triad of
polyarthralgia, tenosynovitis (eg, hand), dermatitis (eg, pustules).
FAS1_2019_11-Musculo.indd 468 11/7/19 5:23 PM